A) hilum
B) renal pelvis
C) renal cortex
D) renal medulla
E) renal sinus
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
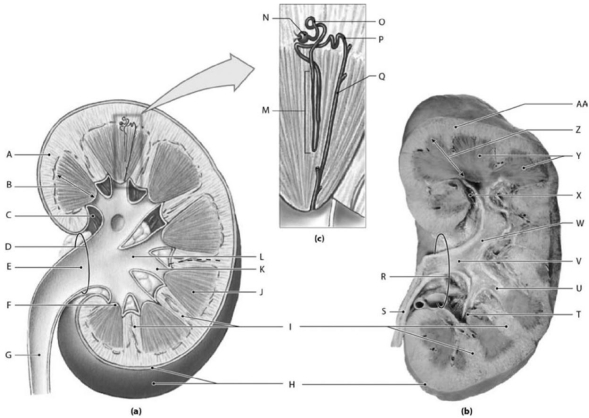 Photo Credit: Ralph T. Hutchings
Figure 18-1 The Structure of the Kidney
Use Figure 18-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label D represents which of the following structures?
Photo Credit: Ralph T. Hutchings
Figure 18-1 The Structure of the Kidney
Use Figure 18-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label D represents which of the following structures?
A) hilum
B) renal pelvis
C) renal cortex
D) renal medulla
E) renal sinus
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Acid-base balance exists when
A) there is a balance between the rates of absorption across the digestive tract with rates of loss at the kidneys.
B) the amount of water gain equals the amount of water loss.
C) protein intake equals protein excretion.
D) the net gain in sodium ions equals its net loss.
E) the production of hydrogen ions is equal to their loss.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The micturition reflex center consists of afferent sensory fibers in the pelvic nerves, which carry the resulting impulses to the
A) hypothalamus.
B) medulla oblongata.
C) pons.
D) lumbar spinal cord.
E) sacral spinal cord.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the nephron, angiotensin II triggers ________ to elevate glomerular pressures and glomerular filtration rates.
A) vasoconstriction of the efferent arterioles
B) vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles
C) vasodilation of the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta
D) vasodilation of the efferent arterioles
E) the release of ANP
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hormone ANP
A) stimulates ADH secretion.
B) increases the rate of sodium ion reabsorption.
C) decreases glomerular filtration.
D) decreases urinary water loss.
E) promotes the dilation of glomerular capillaries.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the level of ADH (antidiuretic hormone) increases,
A) the rate of sodium ion reabsorption in the DCT decreases.
B) more concentrated urine is produced.
C) less water is reabsorbed by the nephron and collecting duct.
D) the water content of urine increases.
E) the sensation of thirst is inhibited.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If through injury, both the blood flow to the kidneys and the glomerular filtration pressure decrease, which of the following will likely occur?
A) The renin-angiotensin system will be activated.
B) Sodium reabsorption will be inhibited.
C) Vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles and glomerular capillaries.
D) Vasodilation of the efferent arterioles and glomerular capillaries.
E) The amount of ADH released in the blood will decrease.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a primary function of the distal convoluted tubule?
A) reabsorption of vital nutrients from the tubular fluid
B) conduction of urine to the minor calices
C) determines the final osmotic concentration and volume of the urine
D) active secretion of ions, acids, drugs, and toxins
E) filtration of plasma to initiate urine formation
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does the peritubular fluid of the renal medulla contain an unusually high solute concentration?
A) The cells of the juxtaglomerular complex secrete the hormone erythropoietin and the enzyme renin.
B) The collecting system reabsorbs water and reabsorbs or secretes sodium, potassium, hydrogen, and bicarbonate ions.
C) The cells of the proximal convoluted tubule reabsorb organic nutrients, plasma proteins, and ions from the tubular fluid.
D) The ascending limb of the nephron loop actively transports sodium and chloride ions out of the tubular fluid.
E) The filtration slits between the slender processes of the podocytes prevent the passage of blood cells and most plasma proteins.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Photo Credit: Ralph T. Hutchings
Figure 18-1 The Structure of the Kidney
Use Figure 18-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label P represents which of the following structures?
Photo Credit: Ralph T. Hutchings
Figure 18-1 The Structure of the Kidney
Use Figure 18-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label P represents which of the following structures?
A) nephron loop
B) renal corpuscle
C) proximal convoluted tubule
D) distal convoluted tubule
E) collecting duct
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Photo Credit: Ralph T. Hutchings
Figure 18-1 The Structure of the Kidney
Use Figure 18-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label N represents which of the following structures?
Photo Credit: Ralph T. Hutchings
Figure 18-1 The Structure of the Kidney
Use Figure 18-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label N represents which of the following structures?
A) nephron loop
B) renal corpuscle
C) proximal convoluted tubule
D) distal convoluted tubule
E) collecting duct
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Organic acids, or metabolic acids, are generated during the normal process of
A) metabolism.
B) metabolic generation of water.
C) exhalation.
D) reabsorption.
E) active secretion.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will likely occur if glomerular blood pressure falls significantly?
A) Excretion of waste products will increase.
B) Kidney filtration will stop.
C) There will be no effect on pH control.
D) Active secretion will occur normally in the distal convoluted tubule.
E) The renin-angiotensin system is unaffected.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 114 of 114
Related Exams