A) sensory adaptation → stimulus reception → sensory transduction → sensory perception.
B) stimulus reception → sensory transduction → sensory perception → sensory adaptation.
C) sensory perception → stimulus reception → sensory transduction → sensory adaptation.
D) sensory perception → sensory transduction → stimulus reception → sensory adaptation.
E) stimulus reception → sensory perception → sensory adaptation → sensory transduction.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Optic neuritis is a condition where the optic nerve is inflamed,leading to loss of the myelin sheath surrounding the optic nerve.What is the likely outcome of optic neuritis?
A) The eye will be unable to focus on distant objects.
B) Action potentials will travel slower through the optic nerve,and vision will be impaired.
C) The right side of the visual field will be transposed with the left.
D) Rods and cones will be more sensitive to light.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sound waves arriving at a listener first strike the
A) tectorial membrane.
B) tympanic membrane.
C) hair cell membrane.
D) basilar membrane.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A researcher is interested in determining whether mice can remember the location of a piece of cheese in a maze.Which of the following results best supports the hypothesis that mice can remember the location of the cheese?
A) an increase in the number of synapses between neurons in the hippocampus
B) an increase in the number of synapses between neurons in the hypothalamus
C) a decrease in the number of synapses between neurons in the hypothalamus
D) a decrease in the number of synapses between neurons in the hippocampus
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What vertebrate brain structure coordinates the biological clock?
A) pituitary gland
B) hypothalamus
C) cerebrum
D) cerebellum
E) thalamus
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
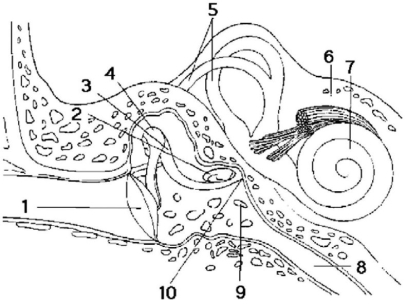 Figure 38.3
-Hair cells are found in the structures represented by which two numbers in Figure 38.3?
Figure 38.3
-Hair cells are found in the structures represented by which two numbers in Figure 38.3?
A) 1 and 2
B) 3 and 4
C) 5 and 7
D) 6 and 8
E) 9 and 10
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A ligand for the umami receptor in the sense of taste is
A) glucose.
B) sodium ions.
C) potassium ions.
D) hydrogen ions.
E) monosodium glutamate.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The middle ear converts
A) air pressure waves to fluid pressure waves.
B) air pressure waves to nerve impulses.
C) fluid pressure waves to nerve impulses.
D) pressure waves to hair cell movements.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the following events are arranged in the order in which they occur for an animal hiding and holding still in response to seeing a predator,which is the fourth event in the series?
A) signaling by an afferent PNS neuron
B) signaling by an efferent PNS neuron
C) information processing in the CNS
D) activation of a sensory receptor
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
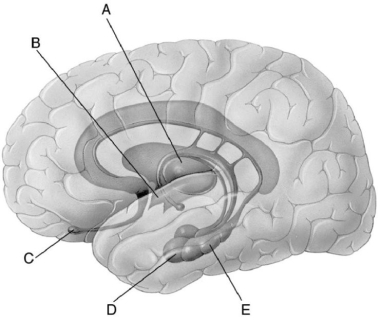 Figure 38.1
-One day,a man woke up and was unable to smell anything around him.Which structure labeled in Figure 38.1 may be affected?
Figure 38.1
-One day,a man woke up and was unable to smell anything around him.Which structure labeled in Figure 38.1 may be affected?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Umami perception would be stimulated by
A) sugar water.
B) chocolate milk.
C) a savory and rich cheese.
D) acidic orange juice.
E) salt water.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The blood-brain barrier
A) filters the entry of solutes from the blood into the cerebrospinal fluid.
B) is formed by oligodendrocytes.
C) tightly regulates the intracellular environment of the CNS.
D) uses chemical signals to communicate with the spinal cord.
E) provides support to the brain tissue.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the human retina,
A) cone cells can detect color,but rod cells cannot.
B) cone cells are more sensitive than rod cells to light.
C) cone cells,but not rod cells,have a visual pigment.
D) rod cells are most highly concentrated in the center of the retina.
E) rod cells require higher illumination for stimulation than do cone cells.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cellular membrane across which ion flow varies during auditory transduction is the
A) tectorial membrane.
B) tympanic membrane.
C) hair cell membrane.
D) basilar membrane.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the correct match of brain structure with one of its primary functions.
A) frontal lobe-decision making
B) occipital lobe-control of skeletal muscles
C) temporal lobe-visual processing
D) cerebellum-language comprehension
E) occipital lobe-speech production
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Eating habanero peppers (which are very spicy!) would activate what type of channel?
A) calcium channels sensitive to cold temperature
B) calcium channels sensitive to hot temperature
C) sodium channels sensitive to cold temperature
D) sodium channels sensitive to hot temperature
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Josue is a 55-year-old male who is experiencing difficulties with speaking,even though he can understand language (as evidenced by his ability to write thoughtful responses after someone asks him a question) .What part of his brain is likely affected?
A) Broca's area
B) Wernicke's area
C) amygdala
D) hippocampus
E) somatosensory cortex
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 38.1
-A woman suffered a brain injury such that she is having trouble with short-term memory formation and recollection.Which structure labeled in Figure 38.1 may be affected?
Figure 38.1
-A woman suffered a brain injury such that she is having trouble with short-term memory formation and recollection.Which structure labeled in Figure 38.1 may be affected?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A given photon of light may trigger an action potential with thousands of times more energy because the signal strength is magnified by
A) the receptor.
B) an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
C) sensory adaptation.
D) triggering several receptors at once.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sensation of hunger triggers the mouse to leave its den to hunt the scorpions.Where would you expect to see a high level of activity in the mouse's brain when it feels hungry?
A) on the outer edges
B) near the middle
C) at the bottom
D) only on the left side
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 105
Related Exams