A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following forms an ionic solid?
A) Cr
B) C4H9NH2
C) Cs NO3
D) N O4
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How much energy is required to vaporize 98.6 g of ethanol (C2H5OH) at its boiling point if its ΔvapH is 40.5 kJ mol-1?
A) 86.7 kJ
B) 11.5 kJ
C) 18.9 kJ
D) 52.8 kJ
E) 39.9 kJ
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the type of solid for argon.
A) metallic atomic solid
B) ionic solid
C) nonbonding atomic solid
D) molecular solid
E) networking atomic solid
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enthalpy change for converting 1.00 mol of ice at -60.0°C to water at 80.0°C is  The specific heats of ice, water, and steam are
The specific heats of ice, water, and steam are 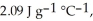
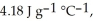 and
and 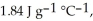 respectively. For
respectively. For 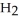 O,
O, 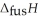 = 6.01 kJ mol-1, and
= 6.01 kJ mol-1, and 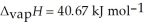 .
.
A) 9.77
B) 14.29
C) 8282
D) 13.17
E) 48.95
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Describe the difference between the conduction band and the valence band.
Correct Answer

verified
The valence band is the group of highest...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Choose the pair of substances that are most likely to form a homogeneous solution.
A) CCl4 and SCl2
B) NF3 and SO2
C) CO and C6H6
D) NH2CH3 and CH4
E) None of the pairs above will form a homogeneous solution.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the compound that exhibits hydrogen bonding as its strongest intermolecular force.
A) SCl2
B) C2H6
C) CH3OH
D) CH2F2
E) None of the above compounds exhibit hydrogen bonding.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the total quantity of heat required to convert 25.0 g of liquid CCl4(l) at 35.0 °C to gaseous CCl4 at 76.8 °C (the normal boiling point for CCl4) . The specific heat of CCl4(l) is 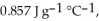 its heat of fusion is
its heat of fusion is 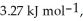 and its heat of vaporization is
and its heat of vaporization is 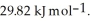
A) 0.896 kJ
B) 1.43 kJ
C) 5.74 kJ
D) 6.28 kJ
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enthalpy change for converting 10.0 g of ice at -25.0 °C to water at 80.0 °C is ________ kJ. The specific heats of ice, water, and steam are 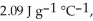
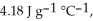 and
and 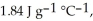 respectively. For
respectively. For 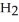 O,
O, 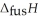 = 6.01 kJ mol-1, and
= 6.01 kJ mol-1, and 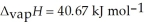 .
.
A) 7.21
B) 6.16
C) 3870
D) 63.97
E) 26.46
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the term used to describe the ability of a liquid to flow against gravity up a narrow tube.
A) capillary action
B) viscosity
C) surface tension
D) density
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the substance with the lowest boiling point.
A) H2S
B) NBr3
C) F2
D) CF2H2
E) H2O2
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the substance with the highest boiling point.
A) CH4
B) CH3CH3
C) CH3CH2Cl
D) CH3CH2CH2OH
E) H2
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of bonding does Sr form upon solidification?
A) covalent network
B) ionic
C) metallic
D) molecular
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vanadium crystallizes in a body-centred cubic structure and has an atomic radius of 131 pm. Determine the density of vanadium if the edge length of a bcc structure is 4r/ 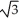 .
.
A) 3.06 g cm-3
B) 12.2 g cm-3
C) 6.11 g cm-3
D) 2.77 g cm-3
E) 8.46 g cm-3
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the figure above, the boiling point of diethyl ether under an external pressure of 1.32 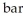 is ________ °C.
is ________ °C.
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 40
E) 0
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following substances would you predict to have the highest ΔvapH?
A) Xe
B) C6H6
C) SiF4
D) Br2
E) N2
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Why is the ΔvapH higher than ΔfusH for a given compound?
Correct Answer

verified
Vaporizing a substance requires the complete "breaking" of all intermolecular attractions, whereas the melting of a substance only requires the breaking of a portion of the intermolecular attractions.
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of intermolecular force causes the dissolution of CH3CH2OH in water?
A) hydrogen bonding
B) dipole-dipole forces
C) ion-dipole forces
D) dispersion forces
E) none of the above
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the vapour pressure (in mbar) of a substance at 36 °C whose normal boiling point is 84 °C and has a ΔvapH of 22.1 kJ mol-1.
A) 319 mbar
B) 31.8 mbar
C) 41.8 mbar
D) 147 mbar
E) 98 mbar
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 144
Related Exams