A) The standard cell potential is -3.63 V.
B) The standard cell potential is -2.11 V.
C) The standard cell potential is -2.11 V..
D) The standard cell potential is -3.63 V..
E) The standard cell potential is 2.11 V.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Batteries used in watches contain mercury(II) oxide. As the current flows, mercury(II) oxide is reduced to mercury according to the following reaction: HgO(s) + H2O( ) + 2 e- ? Hg( ) + 2 OH-(aq) If 2.3 × 10-5 amperes flows continuously for 1200 days, calculate the mass of mercury, Hg( ) , produced.
A) 2.5 g
B) 5.0 g
C) 9.9 g
D) 13 g
E) 15 g
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate ΔrG° for the disproportionation reaction of copper(I) ion (Cu+) at 25 °C. 2 Cu+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + Cu(s) The standard reduction potentials are as follows: Cu+(aq) + e- → Cu(s) E° = +0.518 V Cu2+(aq) + 2 e- → Cu(s) E° = +0.337 V
A) -165 kJ/mol⋅rxn
B) -135 kJ/mol⋅rxn
C) -34.9 kJ/mol⋅rxn
D) +17.5 kJ/mol⋅rxn
E) +135 kJ/mol⋅rxn
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: Cr3+(aq) + 3 e- → Cr(s) ; E° = -0.74 V Fe2+(aq) + 2 e- → Fe(s) ; E° = -0.41 V Calculate the standard Gibbs free energy change for the following reaction. 2 Cr(s) + 3 Fe2+ → 3 Fe(s) + 2 Cr3+(aq)
A) 191 kJ
B) 63.7 kJ
C) -504 kJ
D) -191 kJ
E) 1060 kJ
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true concerning the voltaic cell shown below? 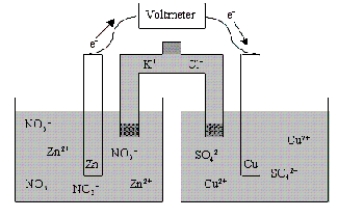
A) The Zn anode mass decreases as the cell discharges.
B) The Zn cathode mass increases as the cell discharges.
C) The Zn cathode mass decreases as the cell discharges.
D) The Zn anode mass increases as the cell discharges.
E) The mass of the Zn electrode neither increases nor decreases as the cell discharges.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true for the following reaction, assuming the given reaction proceeds in the forward direction? Fe3+(aq) + Co(s) → Fe2+(aq) + Co2+(aq)
A) Fe3+(aq) is oxidized and Co(s) is reduced.
B) Fe3+(aq) is oxidized and Co2+(aq) is reduced.
C) Co(s) is oxidized and Fe3+(aq) is reduced.
D) Co(s) is oxidized and Co2+(aq) is reduced.
E) Fe2+(aq) is oxidized and Co(s) is reduced.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cell potential of the following electrochemical cell is determined by using an unspecified concentration of acid. Calculate the pH of the acid solution, given that the measured cell potential is -0.431 V and the anode reduction potential (E°) is 0.222 V at 25 °C. Ag(s) | AgCl(s) | Cl−(aq, 1.0 M) || H+(aq) | H2(g, 1.0 atm) | Pt(s)
A) 3.53
B) 11.0
C) 4.03
D) 7.06
E) 3.47
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If ?rG° for the following reaction is -22.2 kJ/mol-rxn, calculate for the following reaction: Cu2+(aq) + 2 Ag(s) + 2 Cl-(aq) ? Cu(s) + 2 AgCl(s)
A) -0.460 V
B) -0.115 V
C) +0.115 V
D) +0.230 V
E) +0.559 V
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following cell reaction, the standard cell potential is 1.34 V. To determine the cell potential at nonstandard conditions, what is the value that should be used for n in the Nernst equation?
A) 8
B) 10
C) 5
D) 2
E) 6
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning voltaic cells is not true?
A) A salt bridge allows cations and anions to move between half-cells.
B) Electrons flow from a cathode to an anode in the external circuit.
C) Oxidation occurs at an anode.
D) A voltaic cell can be used as a source of energy.
E) A voltaic cell consists of two half-cells.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Write a balanced half-reaction for the reduction of hydrogen peroxide to water in an acidic solution.
A) 2 H2O2( ) ? 2 H2O( ) + O2(g)
B) 2 H2O2( ) + 2e- ? 2 H2O( ) + O2(g)
C) H2O2( ) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 e- ? 2 H2O( )
D) H2O2( ) + 4 H+(aq) + 2 e- ? 2 H2O( ) + H2(g)
E) H2O2( ) + 2 H+(aq) + 4 e- ? 2 H2(g) + O2(g)
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following equations represents the Nernst equation?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Balance the following half-reaction occurring in an acidic solution. NO3-(aq) → NO(aq)
A) NO3-(aq) + 4 H+(aq) + 3 e− → NO(g) + 2 H2O(l)
B) NO3-(aq) + 2 H2O(l) + 3 e− → NO(g) + 4 H+(aq)
C) NO3-(aq) + 4 H+(aq) → NO(g) + 2 H2O(l) + 3 e−
D) NO3-(aq) + 3 e− → NO(g) + 4 H+(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
E) NO3-(aq) + 4 H+(aq) → NO(g) + 2 H2O(l)
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The standard cell potential of the given electrochemical cell is 0.19 V. Pt | Sn4+(aq, 1.0 M) , Sn2+(aq, 1.0 M) || Cu2+(aq, 0.200 M) | Cu Which of the following factors will increase the measured cell potential of the given electrochemical cell?
A) Switching from a platinum to a graphite anode
B) Increasing the size of the anode
C) Decreasing the concentration of Cu2+
D) Increasing the concentration of Sn4+
E) Decreasing the temperature of the cell
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What half-reaction occurs at the cathode during the electrolysis of molten potassium bromide?
A) K(s) → K+(l) + e-
B) Br2(l) + 2 e- → 2 Br-(l)
C) 2 Br-(l) → Br2(l) + 2 e-
D) 2 K+(l) + 2 e- → 2 K(l)
E) 2 H2O(l) + 2 e- → H2(g) + 2 OH-(l)
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true for a product-favored reaction at equilibrium?
A) ΔrG° < 0; E°cell > 0
B) ΔrG° > 0; E°cell < 0
C) ΔrG° < 0; E°cell < 0
D) ΔrG° > 0; E°cell > 0
E) ΔrG° > 0; E°cell = 0
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate Ecell for the following electrochemical cell at 25 °C Pt(s) | H2(g, 1.00 atm) | H+(aq, 1.00 M) || Sn2+(aq, 0.350 M) , Sn4+(aq, 0.020 M) | Pt(s) The standard reduction potentials are as follows: Sn4+(aq) + 2 e- → Sn2+(s) E° = +0.15 V 2 H+(aq) + 2 e- → H2(g) E° = 0.00 V
A) -0.19 V
B) +0.08 V
C) +0.11 V
D) +0.19 V
E) +0.22 V
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The use of electrical energy to produce chemical change is known as _____. An example of this process is the reduction of sodium chloride, NaCl( ), to produce solid sodium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the cell notation below, which of the following species is undergoing reduction? Ni | Ni2+(aq) || Mn2+(aq) | MnO2(s) | Pt(s)
A) Mn2+(aq)
B) Ni2+(aq)
C) Ni(s)
D) MnO2(s)
E) Pt(s)
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the cell notation for a cell in which the hydrogen electrode is the anode and the cathode half-reaction is Co3+(aq) + e− → Co2+(aq) ?
A) Pt(s) | H2(g) | H+(aq) || Co3+(aq) , Co2+(aq) | Pt(s)
B) Pt(s) | H2(g) | H+(aq) || Co3+(aq) , Co2+(aq)
C) Co2+(aq) , Co3+(aq) || H+(aq) | H2(g) | Pt(s)
D) Pt(s) | Co2+(aq) , Co3+(aq) || H+(aq) | H2(g) | Pt(s)
E) H2(g) | H+(aq) || Co2+(aq) , Co3+(aq)
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 83
Related Exams