A) Galileo
B) Copernicus
C) Tycho Brahe
D) Newton
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The light-gathering power of a telescope depends directly on the
A) area of the final aperture of its eyepiece.
B) focal length of its primary mirror or lens.
C) ratio of the focal lengths of its primary element (mirror or lens) and its eyepiece.
D) area of its primary mirror or lens.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these combinations of components of a telescope will produce the worst angular resolution?
A) smaller diameter lens or mirror or radio dish and longer wavelength electromagnetic radiation
B) larger diameter lens or mirror or radio dish and shorter wavelength electromagnetic radiation
C) larger diameter lens or mirror or radio dish and longer wavelength electromagnetic radiation
D) smaller diameter lens or mirror and shorter wavelength electromagnetic radiation
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An object oscillates in one of the patterns shown by Figure 3-43. It might be a particularly interesting astronomical source because these patterns are well-suited to produce 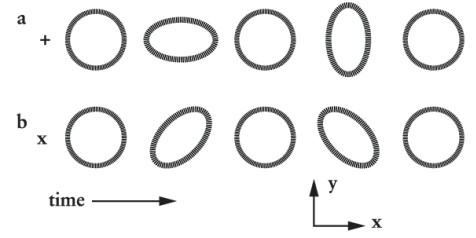
A) supernovae.
B) Balmer line emission.
C) ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays.
D) gravitational waves.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who was the first person to suggest that light is an electromagnetic wave?
A) Thomas Young
B) Isaac Newton
C) Albert Einstein
D) James Clerk Maxwell
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average distance of Pluto from the Sun is 40 au. How long does it take for light to travel across the solar system from one side of Pluto's orbit to the other?
A) 5 ½ hours
B) 8 minutes
C) 22 hours
D) 11 hours
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Hubble Space Telescope, placed in orbit by the space shuttle Discovery in 1990, has a primary mirror of diameter
A) 57 m.
B) 1 m.
C) 6 m.
D) 2.4 m.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Hubble Space Telescope is NOT designed to investigate
A) visible light.
B) ultraviolet radiation.
C) infrared radiation.
D) radio radiation.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The major reason astronomers seek funds to build larger telescopes is to
A) measure a wider spectrum of light from stars.
B) collect more light from distant objects.
C) provide magnified images of stars.
D) bring stars closer to Earth.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is 3 × 108 m/s divided by 500 nm?
A) 6 × 105 meters per second
B) 6 × 1014 per second
C) 6 × 107 meters per nanometer
D) 6 × 1014 meters per second
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What prevented Ole Rømer from calculating an accurate value for the speed of light from his measurements of the delays in eclipse times of Jupiter's moons?
A) The dimensions of the solar system, particularly the length of 1 au, were not known very accurately.
B) Telescopes were not good enough at that time to show Jupiter's moons clearly, and accurate timings were not possible.
C) The distance between Earth's orbit and Jupiter's orbit was unknown.
D) The clocks available at that time were not sufficiently accurate.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his double-slit experiment, Thomas Young used just a single color of light. Suppose he had used a mixture of two colors. What result would he have obtained?
A) The two waves would have canceled each other out, and he would have seen nothing. This is why he used only one color.
B) Two patterns would have formed, one on each color, exactly on top of each other.
C) Two similar patterns would have formed with the light of the shorter wavelength forming the more closely spaced pattern.
D) Two similar patterns would have formed with the light of the longer wavelength forming the more closely spaced pattern.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does angular resolution for a given diameter of a telescope depend on wavelength?
A) Angular resolution worsens as wavelength increases.
B) Angular resolution may improve or worsen as wavelength increases, depending on other factors such as intensity and spectral range (e.g., optical, infrared, radio) .
C) Angular resolution improves as wavelength increases.
D) Angular resolution depends only on the diameter of the telescope and is independent of wavelength.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these can travel at the speed of light in a vacuum?
A) visible light, radio waves, X-rays, and gamma rays
B) only visible light; all other electromagnetic waves travel slower than the speed of light.
C) visible light, atoms, X-rays, and subatomic particles (e.g., electrons)
D) visible light, infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation, and subatomic particles (e.g., electrons)
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the important difference between modern neutrino detectors and the chlorine-argon detection system of previous decades?
A) The new detectors are smaller and thus can be built more cheaply.
B) The new detectors can be tuned to detect neutrinos of any energy.
C) The new detectors are able to detect all three neutrino types, not just those originally emitted from the Sun.
D) The new detectors are in orbit above our atmosphere, thus avoiding the loss of neutrinos absorbed in Earth's atmosphere.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When light in air or a vacuum enters the plane surface of a dense, transparent medium at an angle to the perpendicular to this surface, which way does the light ray bend?
A) The light ray bends away from the perpendicular.
B) The light ray does not bend at all because the material is transparent.
C) The light ray bends toward the perpendicular.
D) The light ray bends so that, whatever the incoming angle, the light travels along the perpendicular to the surface.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The charge-coupled device (CCD) , now used extensively for astronomical imaging, works on what principle?
A) Light from the image modifies the plastic material on a disk, which can then be read on a standard video compact disk (CD) player.
B) A single optical detector generates an electrical signal as it is scanned quickly across the astronomical image.
C) Light generates electrical charge on a computer-readable multi-element array of detectors.
D) Light from the image is detected by new, high-sensitivity, fine-grain, automatically processed film.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 3-43 shows two examples of 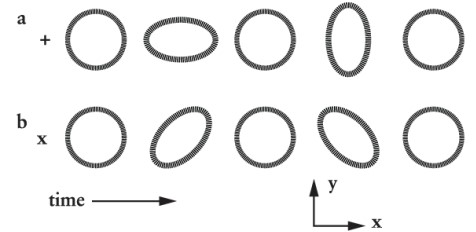
A) quadrupole oscillations.
B) the oscillations causing Cepheid variable stars.
C) features in the cosmic microwave background.
D) cosmic ray showers.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Visible wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation have a range of wavelengths of
A) 400 nm to 700 nm.
B) 1 nm to 100 nm.
C) 800 nm to 1900 nm.
D) 90 nm to 130 nm.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A lens with spherical surfaces suffers from spherical aberration because
A) the lens sags under its own weight, distorting the image.
B) the starlight is distorted by turbulence in Earth's atmosphere.
C) different colors are focused at different distances from the lens.
D) different parts of the lens focus the light at different distances from the lens.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 275
Related Exams