A) MLT-1.
B) ML2T-2.
C) MLT.
D) MLT-2.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A billiard ball is moving in the x direction at 30.0 cm/s and strikes another billiard ball moving in the y direction at 40.0 cm/s. As a result of the collision, the second ball moves at 50.0 cm/s, and the first ball stops. In what final direction does the second ball move?
A) in the x direction
B) at an angle of 45.0o ccw from the x direction
C) at an angle of 53.1o ccw from the x direction
D) Such a collision cannot happen.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three masses are positioned along the x-axis. Their masses and positions are: 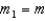 with
with 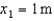 ,
, 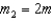 with
with 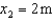 , and
, and  with
with 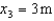 . What is the x-coordinate of center of mass of this system?
. What is the x-coordinate of center of mass of this system?
A) (14/3) m
B) (7/3) m
C) 2 m
D) Not enough information is given to answer this question.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A model car is propelled by a cylinder of carbon dioxide gas. The cylinder emits gas at a rate of 4.5 g/s with an exit speed of 80.0 m/s. The car has a mass of 200 g, including the CO2 cylinder. Starting from rest, what is the car's initial acceleration?
A) 0.90 m/s2
B) 1.8 m/s2
C) 9.0 m/s2
D) 36 m/s2
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The kinetic energy of an object is quadrupled. Its momentum will change by what factor?
A) zero
B) two
C) eight
D) four
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 4.0 ft by 8.0 ft sheet of plywood of uniform density and thickness lies in the 1st quadrant with its long side along the x axis, one corner at the origin, and the diagonally opposite corner at position (x, y) = (8.0 ft, 4.0 ft) . The lower right 2.0 ft by 4.0 ft quarter of the sheet is removed from the sheet. What are the coordinates of the center of mass of the remaining portion of the sheet?
A) (2.0 ft, 4.0 ft)
B) (1.0 ft, 2.0 ft)
C) (3.3 ft, 1.7 ft)
D) (3.3 ft, 2.3 ft)
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2500-kg truck moving at 10.00 m/s strikes a car waiting at a traffic light, hooking bumpers. The two continue to move together at 6.00 m/s. What was the mass of the struck car?
A) 1730 kg
B) 1670 kg
C) 1200 kg
D) 1070 kg
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a system with two moving objects, when a collision occurs between the objects:
A) the total kinetic energy is always conserved.
B) the total momentum is always conserved.
C) the total kinetic energy and total momentum are always conserved.
D) neither the kinetic energy nor the momentum is conserved.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rock is moving with speed v. If the mass of the rock were tripled and the speed were reduced to v/3, which of the following statements would be true?
A) The kinetic energy of the rock is smaller than in the first case, but the momentum is larger.
B) The kinetic energy of the rock is smaller than in the first case, but the momenta of both are the same.
C) The kinetic energies of the rocks are the same in both cases.
D) The kinetic energy of the rock is 1/9 its previous value.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A helicopter stays aloft by pushing large quantities of air downward every second. What mass of air must be pushed downward at 30.0 m/s every second to keep a 1000 kg helicopter aloft?
A) 120 kg
B) 245 kg
C) 327 kg
D) 490 kg
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kaitlin uses a bat to hit a thrown baseball. She knocks the ball back in the direction from which it came in an inelastic collision. The bat, which is heavier than the baseball, continues to move in the same direction after the hit as Kaitlin "follows through." Is the ball moving faster before or after it was hit?
A) The ball was moving faster before it was hit.
B) The ball was moving faster after it was hit.
C) The ball was moving at essentially the same speed before and after the hit.
D) There is insufficient information to answer this problem.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alex throws a 0.15-kg rubber ball down onto the floor. The ball's speed just before impact is 6.5 m/s and just after is 3.5 m/s. If the ball is in contact with the floor for 0.050 s, what is the magnitude of the average force applied by the floor on the ball?
A) 60 N
B) 133 N
C) 30 N
D) 3.5 N
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A neutron in a nuclear reactor makes an elastic head-on collision with a carbon atom initially at rest. (The mass of the carbon atom is 12 times that of the neutron.) What fraction of the neutron's original kinetic energy is retained by the neutron?
A) 14.4%
B) 28.4%
C) 41.4%
D) 71.6%
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A machine gun is attached to a railroad flatcar that rolls with negligible friction. If the railroad car has a mass of 6.25 * 104 kg, how many bullets of mass 25 g would have to be fired at 250 m/s off the back to give the railroad car a forward velocity of 0.3 m/s?
A) 400
B) 2000
C) 3000
D) 5000
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uranium nucleus (mass 238 units) at rest decays into a helium nucleus (mass 4.0 units) and a thorium nucleus (mass 234 units) . If the speed of the helium nucleus is 1.8 * 106 m/s, what is the speed of the thorium nucleus?
A) 1.0 *104 m/s
B) 3.1 * 104 m/s
C) 3.6* 104 m/s
D) 4.1 *104 m/s
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At liftoff, the engines of the Saturn V rocket consumed 14,000 kg/s of fuel and exhausted the combustion products at 2900 m/s. What was the total upward force (thrust) provided by the engines?
A) 3.77 * 107 N
B) 7.54* 107 N
C) 1.47 * 108 N
D) 4.06 * 107 N
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two skaters, both of mass 75 kg, are initially at rest on skates on a frictionless ice pond. One skater throws a 0.3-kg ball at 10 m/s to his friend, who catches it and throws it back at 10 m/s. When the first skater has caught the returned ball, what is the velocity of each of the two skaters?
A) 0.08 m/s, moving apart
B) 0.04 m/s, moving apart
C) 0.08 m/s, moving towards each other
D) 0.04 m/s, moving towards each other
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an automobile collision, how does an airbag lessen the blow to the passenger? Assume as a result of the collision, the passenger stops.
A) The airbag decreases the momentum change of the passenger in the collision.
B) During the collision, the force from the airbag is greater than the force from the windshield or dashboard, so the passenger cannot hit the hard objects.
C) The stopping impulse is the same for either the hard objects or the airbag. Unlike the windshield or dashboard, the airbag gives some, increasing the time for the slowing process and thus decreasing the average force on the passenger.
D) The airbag is there to ensure the seatbelt holds.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The law of conservation of momentum is applicable to systems made up of objects described by which of the following?
A) macroscopic
B) microscopic
C) interacting through friction
D) All the above choices are valid.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A billiard ball (Ball #1) moving at 5.00 m/s strikes a stationary ball (Ball #2) of the same mass. After the elastic collision, Ball #1 moves at a speed of 3.50 m/s. Find the speed of Ball #2 after the collision.
A) 1.25 m/s
B) 1.50 m/s
C) 2.16 m/s
D) 3.57 m/s
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 86
Related Exams