A) 4.13 L
B) 1.01 L
C) 1.38 L
D) 2.76 L
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 25-L container holds ideal hydrogen (H2) gas at a gauge pressure of 0.25 atm and a temperature of 0°C. What mass of hydrogen gas is in this container? The ATOMIC mass of hydrogen is 1.0 g/mol, the ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol ∙ K = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/mol ∙ K, and 1.00 atm = 101 kPa.
A) 1.4 g
B) 2.8 g
C) 4.2 g
D) 5.6 g
E) 6.3 g
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The coefficient of linear expansion of aluminum is 24 × 10-6 K-1 and the coefficient of volume expansion of olive oil is 0.68 × 10-3 K-1. A novice cook, in preparation for deep-frying some potatoes, fills a 1.00-L aluminum pot to the brim and heats the oil and the pot from an initial temperature of 15°C to 190°C. To his consternation some olive oil spills over the top. How much?
A) 0.11 L
B) 0.12 L
C) 0.13 L
D) 0.14 L
E) 0.15 L
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure shows a pV diagram for 0.95 mol of gas that undergoes the process 1 → 2. The gas then undergoes an isochoric heating from point 2 until the pressure is restored to the value it had at point 1. What is the final temperature of the gas? The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol ∙ K = 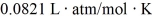 .
. 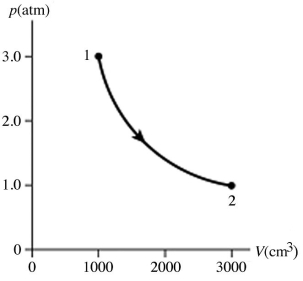
A) -160°C
B) 15°C
C) 390°C
D) 120°C
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You want to insert an aluminum rod, which at 20°C has a radius of 1.000200 cm into a copper tube which has a radius of 1.000100 cm at the same temperature. You decide to put both of them in the refrigerator. At what temperature will the rod just fit if both are cooled to the same temperature? The coefficient of thermal expansion for aluminum is 2.4 × 10-5 K-1, and that of copper is 1.7 × 10-5 K-1.
A) 7.8°C
B) 6.3°C
C) 9.2°C
D) 15°C
E) 5.7°C
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
If a certain sample of an ideal gas has a temperature of 109°C and exerts a pressure of 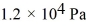 on the walls of its container, how many gas molecules are present in each cubic centimeter of volume? The ideal gas constant is 8.314 J/mol · K and Avogadro's number is
6.022 × 1023 molecules/mol.
on the walls of its container, how many gas molecules are present in each cubic centimeter of volume? The ideal gas constant is 8.314 J/mol · K and Avogadro's number is
6.022 × 1023 molecules/mol.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A hot air balloon has a volume of 2.00 × 103 m3 when fully inflated, and the air inside the balloon is always at atmospheric pressure of 1.01 × 105 Pa because of the large opening used to fill the balloon and heat the air inside it. What is the mass of hot air inside the balloon if its temperature is 120°C? The universal gas constant is 8.314 J/mol ∙ K. (Assume a molecular weight of 28.8 g/mol for air.)
A) 1780 kg
B) 5850 kg
C) 203 kg
D) 62.0 kg
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 3.2-L volume of neon gas (Ne) is at a pressure of 3.3 atm and a temperature of 330 K. The atomic mass of neon is 20.2 g/mol, Avogadro's number is 6.022 × 1023 molecules/mol, and the ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol · K = 0.0821 L · atm/mol · K. The mass of the neon gas is closest to
A) 7.9 × 10-3 kg.
B) 4.6 × 10-3 kg.
C) 3.8 kg.
D) 7.8 kg.
E) 7.8 × 102 kg.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a fixed amount of gas, if the absolute temperature of the gas is doubled, what happens to the pressure of the gas?
A) The answer cannot be determined without volume information.
B) The pressure of the gas becomes double the original pressure.
C) The pressure of the gas becomes eight times the original pressure.
D) The pressure of the gas becomes one half the original pressure.
E) The pressure of the gas becomes four times the original pressure.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which contains more moles of material: 80 grams of helium gas (He, having atomic weight 4.0 g/mol) or 400 grams of argon gas (Ar, having atomic weight 40 g/mol) ?
A) helium
B) argon
C) Both contain the same number of moles.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
3.00 moles of an ideal gas at a pressure of 250 kPa are held in a container of volume of 25.0 L. The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol ∙ K = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/mol ∙ K, and 1 atm = 1.01 × 105 Pa. The temperature of this gas is closest to
A) 240°C.
B) -180°C.
C) 480°C.
D) -1.0°C.
E) -22°C.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A glass flask has a volume of 500 mL at a temperature of 20°C. The flask contains 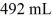 of mercury at
of mercury at 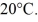 The temperature of the mercury and flask is raised until the mercury reaches the
The temperature of the mercury and flask is raised until the mercury reaches the 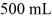 reference mark. The coefficients of volume expansion of mercury and glass are 18 × 10-5 K-1 and 2.0 × 10-5 K-1, respectively. The temperature at which this occurs is closest to
reference mark. The coefficients of volume expansion of mercury and glass are 18 × 10-5 K-1 and 2.0 × 10-5 K-1, respectively. The temperature at which this occurs is closest to
A) 122°C.
B) 112°C.
C) 102°C.
D) 110°C.
E) 132°C.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure shows a pV diagram for 4.3 g of oxygen gas (O2) in a sealed container. The temperature T1 of the gas in state 1 is 21°C. What are the temperatures T3 and T4 of the gas in states 3 and 4? The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol ∙ K = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/mol ∙ K, and the ATOMIC weight of oxygen is 16 g/mol. 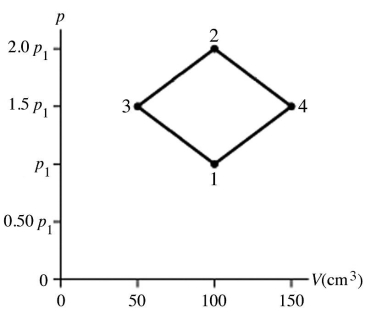
A) -52°C, 390°C
B) 16°C, 47°C
C) 220°C, 660°C
D) 11°C, 32°C
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure shows a 50-kg frictionless cylindrical piston that floats on 0.68 mol of compressed air at 30°C. How far does the piston move if the temperature is increased to 300°C? 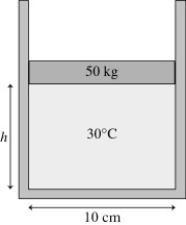
A) 120 cm
B) 250 cm
C) 130 cm
D) 1300 cm
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two steel spheres are made of the same material and have the same diameter, but one is solid and the other is hollow. If their temperature is increased by the same amount,
A) the solid sphere becomes bigger than the hollow one.
B) the hollow sphere becomes bigger than the solid one.
C) the two spheres remain of equal size.
D) the solid sphere becomes heavier and the hollow one becomes lighter.
E) the solid sphere becomes lighter and the hollow one becomes heavier.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The number of molecules in one mole of a substance
A) depends on the molecular weight of the substance.
B) depends on the atomic weight of the substance.
C) depends on the density of the substance.
D) depends on the temperature of the substance.
E) is the same for all substances.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A machinist needs to remove a tight fitting pin of material A from a hole in a block made of material B. The machinist heats both the pin and the block to the same high temperature and removes the pin easily. What statement relates the coefficient of thermal expansion of material A to that of material B?
A) Material B has a greater coefficient of expansion than does material A.
B) The situation is not possible because heating block B will shrink the hole in the material as the material expands with increasing temperature.
C) Material B has the same coefficient of expansion as does material A.
D) Material A has a greater coefficient of expansion than does material B.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fixed amount of ideal gas is held in a rigid container that expands negligibly when heated. At 20°C the gas pressure is p. If we add enough heat to increase the temperature from 20°C to 40°C, the pressure will be
A) impossible to determine since we do not know the number of moles of gas in the container.
B) greater than 2p.
C) less than 2p.
D) equal to 2p.
E) impossible to determine since we do not know the volume of gas in the container.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the temperature of an iron sphere is increased,
A) its density will increase.
B) its volume will decrease.
C) its density will decrease.
D) its mass will decrease.
E) its density will remain unchanged.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hole for a bolt in a brass plate has a diameter of 1.200 cm at 20°C. What is the diameter of the hole when the plate is heated to 220°C? The coefficient of linear thermal expansion for brass is 19 × 10-6/°C. (Express your answer to 4 significant figures.)
A) 1.205 cm
B) 1.125 cm
C) 1.195 cm
D) 1.200 cm
E) 1.210 cm
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 46
Related Exams