A) 5
B) 4
C) 3
D) 6 or more
E) 2
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Utility
A) can be measured with the appropriate equipment.
B) is not real as we cannot measure it directly.
C) is very difficult to observe empirically.
D) is an objective measure of a good's value.
E) measures the common value of a good, independent of the individual.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a consumer can purchase only two goods, beef and chicken. If the price of beef falls (with all other variables held constant) , and the consumption of chicken increases, we can conclude that the increased consumption of chicken is due to
A) a change in the consumer's preference toward chicken.
B) the substitution effect only.
C) the income effect only.
D) neither the income effect nor the substitution effect.
E) both the income effect and the substitution effect.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The income effect refers to the change in quantity demanded that occurs as a result of a change in
A) real income, with relative prices held constant.
B) preferences, with real income held constant.
C) marginal utility, with real income held constant.
D) money income, with relative prices held constant.
E) relative prices, with real income held constant.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The condition required for a consumer to be maximizing utility, for any pair of products, X and Y,is
A) MUX/PY = MUY/PX.
B) MUX = MUY.
C) PX = PY.
D) PX(MUX) = PY(MUY) .
E) MUX/PX = MUY/PY.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the total value (in dollars) that Andrew gets from playing 9-hole rounds of golf. 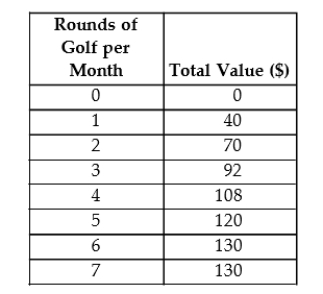 TABLE 6-3
-Refer to Figure 6-1. If this figure represents the utility obtained from consuming units of a good, how many units would this consumer consume if the good were free?
TABLE 6-3
-Refer to Figure 6-1. If this figure represents the utility obtained from consuming units of a good, how many units would this consumer consume if the good were free?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) at least 5
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal rate of substitution measures the tradeoff between the
A) substitution of money for goods.
B) different values that two consumers place on a good.
C) different indifference curves.
D) amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another along an indifference curve.
E) prices of two goods along a budget line.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows a set of budget lines facing a household. 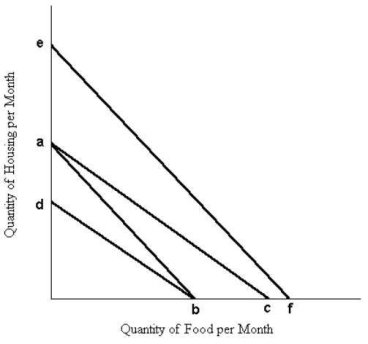 FIGURE 6-7
-Refer to Figure 6-7. The movement of the budget line from ab to ac could be caused by
FIGURE 6-7
-Refer to Figure 6-7. The movement of the budget line from ab to ac could be caused by
A) an increase in the price of food.
B) a decrease in the price of housing.
C) a decrease in the price of food.
D) an increase in money income.
E) an increase in the price of housing.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An individual's consumer surplus from some product can be eliminated entirely by:1. raising the price until very few units are bought.2. charging a price for each unit that is equal to the individual's marginal value for each unit.3. raising the price until zero units are purchased.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 or 3
E) 1, 2, & 3.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a consumer who divides his income between spending on good X and good Y. The opportunity cost of good X in terms of good Y is reflected by the
A) price of good X relative to the prices of all other goods.
B) ratio of the price of X to the price of Y.
C) absolute price of good X.
D) ratio of the price of Y to the price of X.
E) absolute price of good Y.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the pizza market, with a downward-sloping demand curve and an upward-sloping supply curve. Suppose 100 pizzas are purchased at the free-market equilibrium price. The consumer surplus on the 100th pizza is
A) negative.
B) zero.
C) unknown.
D) positive.
E) non-negative.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Indifference theory is based on the assumption that
A) the consumer is able to quantify the difference in total utility received from two different consumption bundles.
B) the consumer receives the same utility and is therefore indifferent between any two consumption bundles.
C) the consumer has equated the marginal utilities of all products, and is therefore indifferent between consumption bundles.
D) consumers can always say which of two consumption bundles they prefer without having to say by how much they prefer it.
E) consumers are not able to rank consumption bundles in order of preference.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If John consumes only two goods, A and B, and he is maximizing his utility subject to his budgetconstraint,
A) MUA/MUB equals the ratio of the price of A to the price of B.
B) MUA/MUB equals 1.
C) MUA/MUB equals the ratio of the total utility of A to the total utility of B.
D) MUA/MUB is at a maximum.
E) MUA/MUB equals zero.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 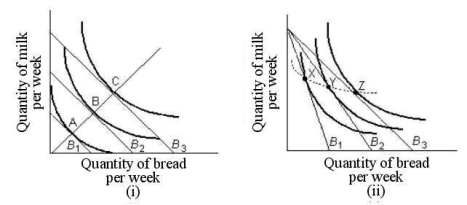 FIGURE 6-8
-Refer to Table 6-1. If the prices of toffee bars and bags of cashews are both $1 and this consumerhas $11 per week to spend on snacks, how many of each will he/she purchase?
FIGURE 6-8
-Refer to Table 6-1. If the prices of toffee bars and bags of cashews are both $1 and this consumerhas $11 per week to spend on snacks, how many of each will he/she purchase?
A) 4 toffee bars and 7 bags of cashews.
B) 5 toffee bars and 5 bags of cashews.
C) 6 toffee bars and 5 bags of cashews.
D) 5 toffee bars and 6 bags of cashews.
E) 3 toffee bars and 8 bags of cashews.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal rate of substitution
A) is equal to the price ratio on the budget line.
B) always has a positive algebraic value.
C) is constant as one moves along a particular indifference curve.
D) is the amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another so as to keep total expenditure unchanged.
E) is the amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another so as to keep total satisfaction unchanged.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a product with an income elasticity greater than one, a price increase will cause the consumer's real income to
A) rise and the quantity purchased to fall.
B) fall and the quantity purchased to rise.
C) fall and the quantity purchased to fall.
D) remain constant.
E) rise and the quantity purchased to rise.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal utility theory is about
A) proving that demand curves are always downward sloping.
B) calculating consumer surplus.
C) the total satisfaction resulting from the consumption of some good by the consumer.
D) the consumer behaviour that underlies the theory of demand.
E) how producers allocate their scarce resources.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a consumer's marginal rate of substitution between X and Y is equal to the ratio of prices forX and Y, and when the consumer is spending all available income, then
A) a higher indifference curve can be reached given the existing budget line.
B) all budget lines are tangent to all indifference curves.
C) the consumer is not maximizing his utility.
D) the budget line is tangent to the indifference curve at all quantities of X and Y.
E) the budget line is tangent to the indifference curve.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The idea that the utility a consumer derives from successive units of a good diminishes as totalconsumption of the good increases is known as
A) diminishing marginal utility.
B) the paradox of value.
C) the utility theory of demand.
D) diminishing total utility.
E) utility maximization.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the total value (in dollars) that Andrew gets from playing 9-hole rounds of golf.  TABLE 6-3
-Refer to Table 6-1. If this consumer purchases 3 toffee bars and 4 bags of cashews per week, his/her total utility will be
TABLE 6-3
-Refer to Table 6-1. If this consumer purchases 3 toffee bars and 4 bags of cashews per week, his/her total utility will be
A) 7
B) 23
C) 31
D) 54
E) 57
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 77
Related Exams