A) stock prices increased during the Great Depression.
B) the U.S. government increased taxes.
C) the U.S. government allowed the money supply to increase.
D) the unemployment rate decreased.
E) expected income increased.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In regard to describing how the economy functions, Keynesian economists claim that
A) more focus should be placed on the long run than the short run.
B) prices are sticky.
C) savings is crucial to growth.
D) the market tends toward stability and full employment.
E) the economy does not need help in moving back to full employment.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the reasons why the Great Depression was so severe is that
A) the U.S. government lowered taxes.
B) stock prices increased during the Great Depression.
C) expected income increased.
D) the U.S. government allowed the money supply to decline.
E) the U.S. government allowed the money supply to increase.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the Great Recession, there was a financial crisis, a stock market crash, and a collapse in housing prices, all of which
A) contributed to a very long and deep recession.
B) helped the U.S. economy perform better than the economies of other countries.
C) kept unemployment from rising above the historical average.
D) resulted in a very short and mild recession.
E) prevented the United States from experiencing a decline in real gross domestic product (GDP) .
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An institutional breakdown in U.S. financial markets would tend to cause
A) aggregate demand to increase.
B) long-run aggregate supply to decrease.
C) short-run aggregate supply to increase.
D) long-run aggregate supply to increase.
E) aggregate demand to decrease.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decline in U.S. wealth would tend to cause _____to_____ .
A) long-run aggregate supply; increase
B) aggregate demand; decrease
C) short-run aggregate supply; increase
D) long-run aggregate supply; decrease
E) aggregate demand; increase
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following graph to answer the next questions. The graph depicts an economy where aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) have decreased, with no change in short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) .
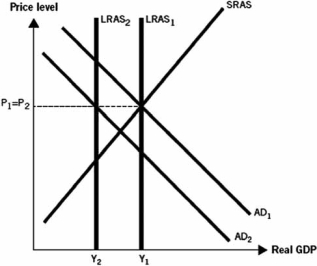 -The decline in housing prices contributed to the Great Recession, as depicted in the graph, in that it
-The decline in housing prices contributed to the Great Recession, as depicted in the graph, in that it
A) caused real gross domestic product (GDP) and the price level to increase.
B) caused an increase in oil and gas prices, which led to inflation.
C) caused a decrease in household wealth and created a crisis in the loanable funds market.
D) caused an increase in household wealth and a crisis in the loanable funds market.
E) prevented unemployment from rising above historical averages.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifted to the left during the Great Depression,
A) tax rates decreased.
B) real gross domestic product GDP) increased.
C) the price level increased.
D) the money supply increased.
E) real gross domestic product GDP) decreased.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following graph to answer the next four questions.
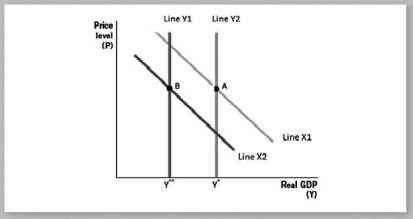 -If point A occurs chronologically before point B, which situation would be depicted?
-If point A occurs chronologically before point B, which situation would be depicted?
A) an increase in aggregate demand and a decrease in long-run aggregate supply
B) a decrease in aggregate demand and a decrease in long-run aggregate supply
C) an increase in aggregate demand and an increase in long-run aggregate supply
D) a decrease in aggregate demand and an increase in long-run aggregate supply
E) a decrease in aggregate demand and a decrease in short-run aggregate supply
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the Great Recession, the unemployment rate climbed as high as________ and remained around 8 percent ________year(s) after the recession began.
A) 15 percent; seven
B) 25 percent; eight
C) 10 percent; five
D) 20 percent; one
E) 35 percent; eight
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a result of several factors, aggregate demand decreased during the Great Depression. One factor was an)
A) increase in consumer sentiment.
B) increase in international trade.
C) decrease in business tax rates.
D) decrease in expected income.
E) increase in the money supply.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When considering the basic operations of the macroeconomy, Keynesian economists argue that
A) the economy does not need help in moving back to full employment.
B) prices are flexible.
C) the market tends toward stability and full employment.
D) savings is a drain on demand.
E) the long run is more significant than the short run.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Macroeconomic policy is
A) the set of laws passed since the Great Depression to influence the macroeconomy.
B) policy enacted by corporations to control prices and output in the macroeconomy.
C) an adjustment of the money supply to influence the macroeconomy.
D) the use of government's budget tools, government spending, and taxes to influence the macroeconomy.
E) all government acts meant to influence the direction of the macroeconomy.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following graph to answer the next questions. The graph depicts an economy where aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) have decreased, with no change in short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) .
 -As a result of aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply decreasing, we can see that the price level _____and real gross domestic product (GDP) _____ .
-As a result of aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply decreasing, we can see that the price level _____and real gross domestic product (GDP) _____ .
A) remained unchanged; decreased
B) increased; decreased
C) decreased; remained unchanged
D) remained unchanged; increased
E) increased; increased
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When compared to other recessions, the Great Depression had
A) very high levels of immigration to the United States.
B) much larger decreases in real gross domestic product (GDP) .
C) very low unemployment.
D) very stable stock prices.
E) much higher levels of consumer sentiment.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following graph to answer the next four questions.
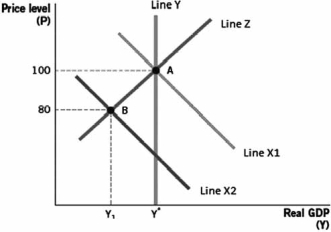 -If point B occurs chronologically before point A, then this graph could represent
-If point B occurs chronologically before point A, then this graph could represent
A) a decrease in aggregate demand with a decrease in long-run and short-run aggregate supply.
B) an increase in aggregate demand with constant long-run and short-run aggregate supply.
C) a decrease in aggregate demand with constant long-run and short-run aggregate supply.
D) constant aggregate demand with a decline in long-run aggregate supply.
E) constant aggregate demand with a decline in short-run aggregate supply.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Great Recession was similar to most other recessions since World War II in that the economy
A) rapidly bounced back and resumed normal growth quickly.
B) never really declined much at all.
C) did not return to normal for at least one year.
D) increased rapidly following the beginning of the recession.
E) essentially collapsed and never recovered.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prior to the Great Depression, U.S. stock prices decreased dramatically. This would tend to cause
A) aggregate demand to decrease.
B) aggregate demand to increase.
C) long-run aggregate supply to increase.
D) short-run aggregate supply to increase.
E) long-run aggregate supply to decrease.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Great Recession was different from other recessions since World War II in that
A) real gross domestic product GDP) initially declined and then recovered sometime later.
B) the trade deficit was largely unaffected.
C) the rate of unemployment increased and then decreased at a later time.
D) the decline in real gross domestic product GDP) was much larger and lasted longer.
E) the economy did not return to normal for at least one year.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When considering the magnitude of the Great Depression in comparison to other recessions, the Great Depression
A) had far higher levels of international trade.
B) was fairly typical, in terms of its length.
C) was very short.
D) was the most severe recession in U.S. history.
E) only affected a small number of Americans.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 175
Related Exams