A) 5/6
B) 11/12
C) 1/12
D) 10/13
E) 11/13
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 900-kg car traveling east at 15.0 m/s suddenly collides with a 750-kg car traveling north at 20.0 m/s. The cars stick together after the collision. In what direction does the wreckage move just after the collision?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two astronauts, of masses 60 kg and 80 kg, are initially right next to each other and at rest in outer space. They suddenly push each other apart. What is their separation after the heavier astronaut has moved 12 m?
A) 28 m
B) 24 m
C) 9.0 m
D) 16 m
E) 21 m
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 50-g ball moving at 10 m/s in the +x direction suddenly collides head-on with a stationary ball of mass 100 g. If the collision is perfectly elastic, what is the velocity of each ball immediately after the collision?
A) +3.3 m/s,-6.7 m/s
B) -3.3m/s,+6.7 m/s
C) -6.7 m/s,+3.3 m/s
D) +6.7 m/s,-3.3 m/s
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An object initially at rest suddenly explodes in two fragments of masses 2.6 kg and 3.3 kg that move in opposite directions. If the speed of the first fragment is 3.6 m/s, find the internal energy of The explosion.
A) 30 J
B) 38 kJ
C) 30 kJ
D) 38 J
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure, determine the character of the collision. The masses of the blocks, and the velocities before and after, are shown. The collision is
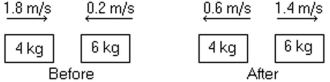
A) completely inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) partially inelastic.
D) characterized by an increase in kinetic energy.
E) not possible because momentum is not conserved.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A railroad car collides with and sticks to an identical railroad car that is initially at rest. After the collision, the kinetic energy of the system
A) is one quarter as much as before.
B) is the same as before.
C) is one third as much as before.
D) is one fourth as much as before.
E) is half as much as before.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you want to double the kinetic energy of a gas molecule, by what factor must you increase its momentum?
A) 16
B) 4
C) 2
D)
E)
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A 14,000-kg boxcar is coasting at 1.50 m/s along a horizontal track when it suddenly hits and couples with a stationary 10,000-kg boxcar. What is the speed of the cars just after the collision?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A batter hits a 0.140-kg baseball that was approaching him at 30 m/s and, as a result, the ball leaves the bat at 40 m/s in the reverse of its original direction. The ball remains in contact with the bat for 2.0 ms. What is the magnitude of the average force exerted by the bat on the ball?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 60.0-kg man stands at one end of a 20.0-kg uniform 10.0-m long board. How far from the man is the center of mass (or center of gravity) of the man-board system?
A) 5.00 m
B) 2.50 m
C) 9.00 m
D) 7.50 m
E) 1.25 m
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a quantity you calculated had units of kg · m/s, what type of quantity could it be? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A) impulse
B) work
C) kinetic energy
D) momentum
E) force
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1200-kg cannon suddenly fires a 100-kg cannonball at 35 m/s. What is the recoil speed of the cannon? Assume that frictional forces are negligible and the cannon is fired horizontally.
A) 35 m/s
B) 3.5 m/s
C) 2.9 m/s
D) 3.2 m/s
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A 1.0-g bead is at (-2.0 cm, 2.0 cm), a 2.0-g bead is at (2.0 cm, -4.0 cm), and a 3.0-g bead is at (2.0 cm, 0.0 cm). What are the coordinates of the center of mass (or center of gravity) of this system of beads?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a game of pool, the white cue ball hits the #5 ball and stops, while the #5 ball moves away with the same velocity as the cue ball had originally. Both balls have the same mass. This type of collision is
A) completely inelastic.
B) elastic.
C) somewhat inelastic.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two astronauts, of masses 60 kg and 80 kg, are initially right next to each other and at rest in outer space. They suddenly push each other apart. How far has the heavier astronaut moved when the lighter astronaut has moved 12 m?
A) 7.0 m
B) 16 m
C) 21 m
D) 9.0 m
E) 12 m
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two objects of different mass have equal, non-zero kinetic energies. Which object has the greater magnitude momentum?
A) the lighter object
B) the heavier object
C) They both have the same magnitude momentum.
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two ice skaters suddenly push off against one another starting from a stationary position. The 45-kg skater acquires a speed of 0.375 m/s relative to the ice. What speed does the 60-kg skater acquire relative to the ice?
A) 0.50 m/s
B) 0.38 m/s
C) 0.00 m/s
D) 0.28 m/s
E) 0.75 m/s
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The momentum of an isolated system is conserved
A) only in elastic collisions.
B) in both elastic and inelastic collisions.
C) only in inelastic collisions.
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A dinner plate falls vertically to the floor and breaks up into three pieces, which slide horizontally along the floor. Immediately after the impact, a 320-g piece moves along the +x -axis with a speed of 2.00 m/s and a 355-g piece moves along the +y -axis with a speed of 1.50 m/s. The third piece has a mass of 100 g. In what direction relative to the +x -axis does the third piece move?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 139
Related Exams