A) ammonia.
B) nitrate.
C) nitrite.
D) urea.
E) uric acid.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Processing of filtrate in the proximal and distal tubules
A) achieves the sorting of plasma proteins according to size.
B) achieves the conversion of toxic ammonia to less toxic urea.
C) maintains homeostasis of pH in body fluids.
D) regulates the speed of blood flow through the nephrons.
E) reabsorbs urea to maintain osmotic balance.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increased ADH secretion is likely after
A) drinking lots of pure water.
B) sweating-induced dehydration increases plasma osmolarity.
C) ingestion of ethanol (drinking alcoholic drinks) .
D) eating a small sugary snack.
E) blood pressure is abnormally high.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The body fluids of an osmoconformer would be ________ with its ________ environment.
A) hyperosmotic; freshwater
B) isotonic; freshwater
C) hyperosmotic; saltwater
D) isoosmotic; saltwater
E) hypoosmotic; saltwater
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The advantage of excreting nitrogenous wastes as urea rather than as ammonia is that
A) urea can be exchanged for Na⁺.
B) urea is less toxic than ammonia.
C) urea requires more water for excretion than ammonia.
D) urea does not affect the osmolar gradient.
E) less nitrogen is removed from the body.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After blood flow is artificially reduced at one kidney, you would expect that kidney to secrete more of the hormone known as
A) erythropoietin.
B) angiotensinogen.
C) renin.
D) antidiuretic hormone.
E) atrial natriuretic peptide.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Excessive formation of uric acid crystals in humans leads to
A) a condition called diabetes, where excessive urine formation occurs.
B) a condition of insatiable thirst and excessive urine formation.
C) gout, a painful inflammatory disease that primarily affects the joints.
D) the absence of urea in the urine.
E) osteoarthritis, an inevitable consequence of aging.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If ATP production in a human kidney was suddenly halted, urine production would
A) come to a complete halt.
B) decrease, and the urine would be hypoosmotic compared to plasma.
C) increase, and the urine would be isoosmotic compared to plasma.
D) increase, and the urine would be hyperosmotic compared to plasma.
E) decrease, and the urine would be isoosmotic compared to plasma.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A necropsy (postmortem analysis) of a marine sea star that died after it was mistakenly placed in fresh water would likely show that it died because
A) it was stressed and needed more time to acclimate to the new conditions.
B) it was so hyperosmotic to the fresh water that it could not osmoregulate.
C) the sea star's kidneys could not handle the change in ionic content presented by the fresh water.
D) its contractile vacuoles ruptured.
E) its cells dehydrated and lost the ability to metabolize.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ADH and RAAS work together in maintaining osmoregulatory homeostasis through which of the following ways?
A) ADH regulates the osmolarity of the blood and RAAS regulates the volume of the blood.
B) ADH regulates the osmolarity of the blood by altering renal reabsorption of water, and RAAS maintains the osmolarity of the blood by stimulating Na⁺ reabsorption.
C) ADH and RAAS work antagonistically; ADH stimulates water reabsorption during dehydration and RAAS causes increased excretion of water when it is in excess in body fluids.
D) both stimulate the adrenal gland to secrete aldosterone, which increases both blood volume and pressure via its receptors in the urinary bladder.
E) by combining at the receptor sites of proximal tubule cells, where reabsorption of essential nutrients takes place.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The osmoregulatory/excretory system of a freshwater flatworm is based on the operation of
A) protonephridia.
B) metanephridia.
C) Malpighian tubules.
D) nephrons.
E) ananephredia.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In animals, nitrogenous wastes are produced mostly from the catabolism of
A) starch and cellulose.
B) triglycerides and steroids.
C) proteins and nucleic acids.
D) phospholipids and glycolipids.
E) fatty acids and glycerol.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Juxtamedullary nephrons can concentrate salt effectively in the renal medulla because of their long
A) loops of Henle.
B) distal convoluted tubules.
C) Bowman's capsules.
D) proximal convoluted tubules.
E) glomeruli.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to wetland mammals, water conservation in mammals of arid regions is enhanced by having more
A) juxtamedullary nephrons.
B) Bowman's capsules.
C) ureters.
D) podocytes.
E) urinary bladders.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In humans, the transport epithelial cells in the ascending loop of Henle
A) are the largest epithelial cells in the body.
B) are not in contact with interstitial fluid.
C) have plasma membranes of low permeability to water.
D) have 50% of their cell mass made of smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
E) are not affected by high levels of nitrogenous wastes.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Freshwater flatworms form a urine that is typically
A) of high solute concentration, in order to conserve body fluids.
B) of very low volume, in order to conserve body fluids.
C) of high solute concentration and very low volume, in order to conserve body fluids.
D) of high solute concentration and of high volume, matching their normal fluid uptake.
E) of low solute concentration and of high volume, matching their normal fluid uptake.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following structural formulas to identify the following items.
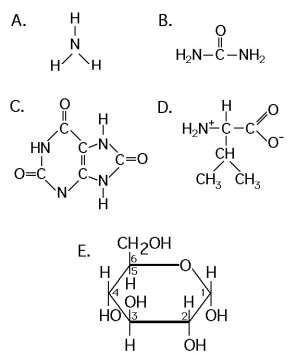 -Which of the following is synthesized by mammals, most amphibians, sharks, and some bony fishes, and has lower toxicity than its nitrogenous substrate?
-Which of the following is synthesized by mammals, most amphibians, sharks, and some bony fishes, and has lower toxicity than its nitrogenous substrate?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Osmoregulatory adjustment via the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system can be triggered by
A) sleeping for one hour.
B) severe sweating on a hot day.
C) eating a bag of potato chips.
D) eating a pizza with olives and pepperoni.
E) drinking several glasses of water.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unlike most bony fishes, sharks maintain body fluids that are isoosmotic to seawater, so they are considered by many to be osmoconformers. Nonetheless, these sharks osmoregulate at least partially by
A) using their gills and kidneys to rid themselves of sea salts.
B) monitoring dehydration at the cellular level with special gated aquaporins.
C) tolerating high urea concentrations that balance internal salt concentrations to seawater osmolarity.
D) synthesizing trimethylamine oxide, a chemical that binds and precipitates salts inside cells.
E) possessing a special adaptation that allows their cells to operate at an extraordinarily high salt concentration.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to the seawater around them, most marine invertebrates are
A) hyperosmotic.
B) hypoosmotic.
C) isoosmotic.
D) hyperosmotic and isoosmotic.
E) hypoosmotic and isoosmotic.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 69
Related Exams