A) 4.69 × 10-4
B) 9.012 × 10-9
C) 6.21 × 10-10
D) 7.41 × 10-11
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a particular reactant is involved in the slowest step of a multistep reaction, then what will be the effect of increasing its concentration?
A) The reaction rate will decrease.
B) The reaction rate will increase.
C) The reaction rate will be unaffected.
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a reaction such as A2(g) + B2(g) → 2AB(g) . What can we say about the mechanism of the reaction?
A) If the reaction is fast, it occurs in a single step.
B) If the reaction is fast, it occurs in multiple steps.
C) If the reaction is slow, it occurs in multiple steps.
D) We must examine each case individually.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a reaction occurs very rapidly even at a relatively low temperature, which of the following is true?
A) The reaction is endothermic.
B) The reaction is exothermic.
C) The reaction has a low activation energy.
D) The reaction must be a single-step reaction.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given that the reaction 2Na2O (s) → 4Na(s) + 2O2(g) is endothermic, which of the following is true of the reaction 4Na(s) + 2O2(g) → 2Na2O(s) ?
A) Its activation energy is lower than that of 2Na2O(s) → 4Na(s) + 2O2(g) .
B) Its activation energy is the same as that of 2Na2O(s) → 4Na(s) + 2O2(g) .
C) Its activation energy is higher than that of 2Na2O(s) → 4Na(s) + 2O2(g) .
D) There is no relationship between its activation energy and that of 2Na2O(s) → 4Na(s) + 2O2(g) .
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate of reaction for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to yield water and oxygen is represented by the following equation: Rate = k[H2O2]. Which of the following is indicated by this equation?
A) The rate of the reaction is unaffected by the concentration of O2.
B) The rate of the reaction will increase with the increasing concentration of H2O2.
C) The rate of the reaction will decrease with the increasing concentration of O2.
D) None of these are indicated by the equation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The temperature effect on reaction rate is the result of which of the following?
A) At higher temperatures, there are more collisions.
B) At higher temperatures, a larger fraction of the collisions are effective collisions.
C) At higher temperatures, there are more collisions and a larger fraction of the collisions are effective collisions.
D) None of these.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Acetic acid is the active ingredient in vinegar. In a solution of acetic acid, the following equilibrium is established. 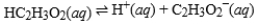 The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 1.5 × 10-5. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 1.5 × 10-5. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 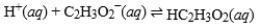
A) 1.8 × 10-5
B) 4.2 × 10-3
C) 6.6 × 104
D) 3.1 × 109
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the study of the rates of chemical reactions?
A) kinetics
B) stoichiometry
C) thermodynamics
D) none of these
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the effect of decreasing the temperature at which a reaction is carried out?
A) In all cases, the rate of reaction decreases.
B) In virtually all cases, the rate of reaction decreases.
C) In all cases, the rate of reaction increases.
D) In virtually all cases, the rate of reaction increases.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction 2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l) + O2(g) , we measure the evolution of gas to determine the rate of reaction. At the beginning of the reaction (at 0 min) , 0.070 L of O2 is present. After 15 min, the volume of O2 is 0.40 L. What is the rate of reaction?
A) 0.022 L/min
B) 0.033 L/min
C) 0.23 L/min
D) 0.33 L/min
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following symbols is used to denote a reversible reaction?
A) →
B) ←
C) ⇌
D) ↔
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can be the equilibrium constant for a reaction that does not yield a significant concentration of products?
A) 4 × 10-1
B) 1 × 10-2
C) 1 × 102
D) 1 × 10-15
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the exothermic reaction 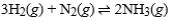 making which of the following changes will ensure that the reaction will not shift either to the left or to the right?
making which of the following changes will ensure that the reaction will not shift either to the left or to the right?
A) raising the temperature and adding NH3
B) lowering the temperature and removing NH3
C) raising the temperature and adding NH3 and lowering the temperature and removing NH3
D) none of these
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following graph. 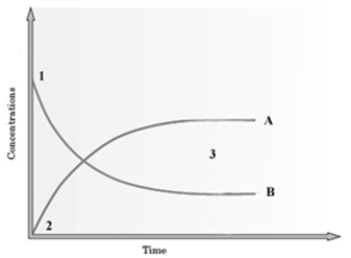 The graph is based on data collected from the following reaction.
The graph is based on data collected from the following reaction. 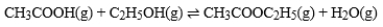 If Curve B presently represents C2H5OH, how would the graph change if this line represented CH3COOH?
If Curve B presently represents C2H5OH, how would the graph change if this line represented CH3COOH?
A) The slope of the line would greater.
B) The slope of the line would be less.
C) The line would be the same.
D) This condition cannot be predicted.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a decrease in temperature affect an endothermic reaction that has not reached equilibrium?
A) The rate of reaction slows, and less product is formed.
B) The rate of reaction slows, but more product is formed.
C) The rate of reaction speeds up, but less product is formed.
D) The rate of reaction speeds up, and more product is formed.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of an equilibrium situation?
A) an unsaturated solution
B) a saturated solution
C) a supersaturated solution
D) all of these
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction ![For the reaction , which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression? A) K = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>]/[H<sub>2</sub>O] B) K = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup>/[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) K = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup>/[H<sub>2</sub>][O<sub>2</sub>] D) K = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]/[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8310/11eb6c44_5842_070a_8d9d_83e3835f63dd_TB8310_11.jpg) , which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression?
, which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression?
A) K = [H2]2 [O2]/[H2O]
B) K = [H2O]2/[H2]2 [O2]
C) K = [H2O]2/[H2][O2]
D) K = [H2]2[O2]/[H2O]2
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of activation energy?
A) Reactions with low activation energies are rapid.
B) The activation energy for an exothermic reaction is negative.
C) The activation energy is the energy difference between the reactants and the products.
D) Reactions with low activation energies have lower number of effective collisions.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a particular chemical reaction, two bonds are broken and no bonds are formed. Based on this information alone, which of the following is true?
A) The reaction has a high activation energy.
B) The reaction is endothermic.
C) The reaction is exothermic.
D) We cannot determine which of the statements is true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 104
Related Exams