A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figures to answer the question.
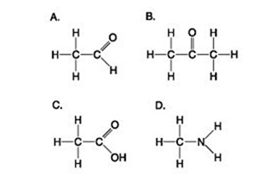 Which molecule(s) shown is (are) ionized in a cell?
Which molecule(s) shown is (are) ionized in a cell?
A) A
B) B and D
C) C and D
D) D
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A carbon atom has 6 electrons however, its valency is 4. This is because the carbon atom ________.
A) donates its 2 electrons to another atom
B) shares its 2 electrons and bonds with another atom
C) has 4 electrons in its first shell and 2 in the second shell
D) has only 2 electrons in its first shell and 4 in the second shell
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes cis-trans isomers?
A) They have variations in arrangement around a double bond.
B) They have an asymmetric carbon that makes them mirror images.
C) They have the same chemical properties.
D) They have different molecular formulas.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The experimental approach taken in current biological investigations presumes that ________.
A) simple organic compounds can be synthesized in the laboratory from inorganic precursors, but complex organic compounds like carbohydrates and proteins can be synthesized only by living organisms
B) a life force ultimately controls the activities of living organisms, and this life force cannot be studied by physical or chemical methods
C) living organisms are composed of the same elements present in nonliving things, plus a few special trace elements found only in living organisms or their products
D) living organisms can be understood in terms of the same physical and chemical laws that can be used to explain all natural phenomena
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A compound contains hydroxyl groups as its predominant functional group. Therefore, this compound ________.
A) lacks an asymmetric carbon and is probably a fat or lipid
B) should dissolve in water
C) should dissolve in a nonpolar solvent
D) will not form hydrogen bonds with water
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figures to answer the question.
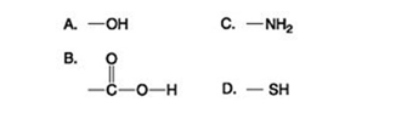 Which of the functional groups shown helps stabilize proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between protein molecules?
Which of the functional groups shown helps stabilize proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between protein molecules?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to a hydrocarbon chain where all the carbon atoms are linked by single bonds, a hydrocarbon chain with the same number of carbon atoms but with one or more double bonds will ________.
A) be more flexible in structure
B) be more constrained in structure
C) be more polar
D) have more hydrogen atoms
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) ADP contains more energy than ATP.
B) Following hydrolysis, ATP can give off one phosphate, whereas ADP cannot.
C) ADP can have two positive charges.
D) ATP can have four negative charges.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the question.
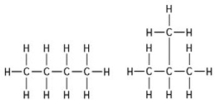 The two molecules shown in the figures are best described as ________.
The two molecules shown in the figures are best described as ________.
A) enantiomers
B) structural isomers
C) cis-trans isomers
D) chain length isomers
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules is a part of ATP?
A) adenosine
B) cytosine
C) guanine
D) uracil
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with other atoms?
A) ionic
B) hydrogen
C) covalent
D) ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figures to answer the question.
 Which of the functional groups shown is present in ethanol but not in ethane?
Which of the functional groups shown is present in ethanol but not in ethane?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Organic chemistry is currently defined as
A) the study of compounds made only by living cells.
B) the study of carbon compounds.
C) the study of natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds.
D) the study of hydrocarbons.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which chemical group is most likely to be responsible for an organic molecule behaving as a base?
A) hydroxyl
B) carbonyl
C) amino
D) phosphate
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
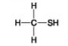
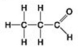
Use the figures to answer the question.
A.
 B.
B.
 C.
C.
 D.
D.
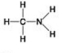
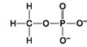 Which molecule shown is a thiol?
Which molecule shown is a thiol?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figures to answer the question.
 Which of the groups is an acidic functional group that can dissociate and release H⁺ into a solution?
Which of the groups is an acidic functional group that can dissociate and release H⁺ into a solution?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the question.
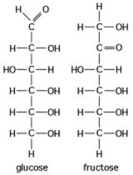 The figure shows the structures of glucose and fructose. These two molecules are ________.
The figure shows the structures of glucose and fructose. These two molecules are ________.
A) isotopes
B) enantiomers
C) cis-trans isomers
D) structural isomers
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Miller's classic experiment demonstrated that a discharge of sparks through a mixture of gases could result in the formation of a large variety of organic compounds. Miller did not use ________ as one of the gases in his experiment.
A) methane
B) oxygen
C) water
D) ammonia
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water?
A) The majority of their bonds are polar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
B) The majority of their bonds are nonpolar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
C) They exhibit considerable molecular complexity and diversity.
D) They are less dense than water.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 58
Related Exams