A) The pH would equal 7.0 at the equivalence point.
B) The pH is determined by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
C) The pH is determined by taking - log[CH3COOH]original.
D) The pH is determined by solving for the pH of a basic salt.
E) The pH is determined by solving for the pH of an acidic salt.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH after the addition of 0.050 moles of NaOH to 1.00 L of a 0.500 M NH3 / 0.500 M NH4Cl buffer solution? Assume that there is no volume change on addition of the NaOH. K b for NH3 = 1.8×10 - 5.
A) 4.74
B) 4.66
C) 9.34
D) 9.17
E) 9.53
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following equilibrium reaction:
NH₃+ H₂ O  NH ₄+ + OH - K b (NH ₃) = 1.8 10 - 5 Qualitatively, what is the effect of adding NaOH to an aqueous solution of NH₃as shown in the equilibrium reaction above?
(Use Le Chatelier s principle.)
NH ₄+ + OH - K b (NH ₃) = 1.8 10 - 5 Qualitatively, what is the effect of adding NaOH to an aqueous solution of NH₃as shown in the equilibrium reaction above?
(Use Le Chatelier s principle.)
A) The equilibrium will shift left favoring the reactant side and the pH will drop.
B) The equilibrium will shift right favoring the product side and the pH will drop.
C) There will be no shift in the equilibrium reaction and the pH will remain constant.
D) The equilibrium will shift left favoring the reactant side and the pH will rise.
E) The equilibrium will shift right favoring the product side and the pH will rise.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of these combinations would give a buffer that would be most effective in the pH range 3.0 tO4.0?
A) 0.10 M CH3COOH, 0.10 M CH3COONa, K a = 1.8×10 - 5
B) 0.10 M NH4Cl, 0.10 M NH3, K b = 1.8×10 - 5
C) 0.10 M HF, 0.10 M NaF, K a = 3.54×10 - 4
D) 0.10 M H2CO3, 0.10 M NaHCO3, K a = 4.30×10 - 7
E) 0.10 M HCl, 0.10 NaCl
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following compounds have very limited solubility in water. Which of the following would dissolve in water under acidic conditions?
A) BaCO3
B) BaSO4
C) PbSO4
D) AgI
E) CuCl
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxalic acid is diprotic with p K al = 1.23 and p K a2 = 4.19. Estimate the pH of a solution of sodium hydrogen oxalate.
A) pH = 3
B) pH = 5
C) pH = 7
D) pH = 9
E) pH = 11
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 25.0 mL volume of 0.100 M aspartic acid (monoprotic) is titrated with 0.100 M NaOH to the equivalence point. If the pH at the equivalence point is 8.28, calculate K a for aspartic acid.
A) 1.4×10 - 4
B) 7.3×10 - 4
C) 5.2×10 - 9
D) 1.9×10 - 6
E) 1.0
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solution of HCOOH ( K a = 1.8×10 - 4) and HCOO - was submitted for chemical analysis. The results were: [HCOOH] = 0.050 M, [HCOO - ] = 0.15 M. Calculate the pH.
A) 4.22
B) 3.74
C) 3.27
D) 1.30
E) - 1.30
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH of an aqueous solution that contains 0.183 M sodium formate (NaCHO2) and 0.300 M in formic acid? K a(HCHO2) = 1.8×10 - 4
A) pH = 3.53
B) pH = 3.96
C) pH = 4.56
D) pH = 5.16
E) pH = 8.13
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the pH in a solution which is made when 20.0 mL of 0.10 M NH3 ( K b = 1.8×10 - 5) is added to 30.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl.
A) 0.02
B) 1.70
C) 4.57
D) 4.74
E) 9.25
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If it takes 32.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl to titrate 25.0 mL of a Ba(OH) 2 solution to the equivalence point, what is the molarity of the original Ba(OH) 2 solution?
A) 0.128 M
B) 3.20×10 - 2 M
C) 0.256 M
D) 6.40×10 - 2 M
E) 0.100 M
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH of an aqueous solution that contains 0.085 M HNO2 and 0.10 M potassium nitrite (KNO2) ? K a(HNO2) = 4.5×10 - 4
A) pH = 3.27
B) pH = 3.42
C) pH = 4.28
D) pH = 4.42
E) pH = 7.87
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following titration curves listed below best represents a curve for the complete titration of citric acid, H3C6H5O7, a triprotic acid with a strong base such as NaOH?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH of the following solution? 20) 0 mL of 0.50 M acetic acid ( K a = 1.8×10 - 5) is added tO5 .00 mL of 0.50 M NaOH.
A) 4.27
B) 4.74
C) 5.22
D) 5.40
E) 7.00
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH of an aqueous solution that contains 0.39 M C6H5COOH and 0.14 M C6H5COONa? K a(C6H5COOH) = 6.3×10 - 5
A) pH = 0.409
B) pH = 3.76
C) pH = 4.65
D) pH = 6.29
E) pH = 8.65
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a buffer solution containing a weak acid, HX, and a salt of the weak acid's conjugate base, NaX. Under what conditions does the pH just equal the p K a of the weak acid?
A) When the p K a equals 7.0.
B) When [HX] > [NaX].
C) When [HX] < [NaX].
D) When [HX] = [NaX].
E) When there is no NaX present.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which experiment listed below would provide a titration curve that resembles the titration shown below?
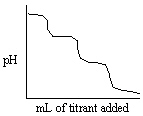
A) Titrating NH3 with standard NaOH (delivered from the burette) .
B) Titrating NH3 with standard HCl (delivered from the burette) .
C) Titrating H3PO4 with standard NaOH (delivered from the burette) .
D) Titrating Na3PO4 with standard HCl (delivered from the burette) .
E) Titrating Na3PO4 with standard NaOH (delivered from the burette) .
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.78 M NH3 and 0.140 M NH4NO3. K b = 1.8×10 - 5 for NH3.
A) 4.00
B) 10.00
C) 4.74
D) 9.26
E) 13.91
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which pair(s) of substances would make a suitable buffer pair combination? I. NaOH and NaBr II. HF and NaF III. CH3NH3+Cl - and CH3NH2
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) II and III
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 25.0 mL volume of a 0.200 M N2H4 solution ( K b = 1.70×10 - 6) is titrated to the equivalence point with 0.100 M HCl. What is the pH of this solution at the equivalence point? The titration is: N2H4 + HCl→N2H5+ + Cl -
A) 4.70
B) 8.23
C) 7.00
D) 9.30
E) 5.77
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 98
Related Exams