A) It increases the rate of the forward reaction.
B) Catalysts decrease the rate of the back reaction.
C) Catalysts lower the activation energy of a reaction.
D) Catalysts decrease the time required for equilibrium to be established.
E) Catalysts never allow equilibrium to be reached
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following graphs depict a reaction proceeding at a constant rate? Select all that apply.
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
F) ![]()
H) E) and F)
Correct Answer

verified
A,B,C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The activation energy of a reaction is equal to which of the following?
A) The energy of the reactants.
B) The energy of the transition state.
C) The Gibbs free energy of the reaction.
D) The energy of the products.
E) The enthalpy change of the reaction.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The units used to express the rate of a chemical reaction are which of the following?
A) mol s-1
B) mol L-1 s-1
C) L mol-1 s-1
D) s mol-1
E) s mol-1 L-1
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An enzyme-catalyzed reaction can be represented by which of the following general equations?
A) E + S ES E + P
B) E + S ⇌ E + P
C) E + S ⇌ ES P
D) ES E + P
E) E + S ⇌ P
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The concentration of a compound, X, is measured at different time intervals during the course of a chemical reaction. After plotting a graph of the concentration of X against time, shown in the graph below, the points labelled A-E on the graph have the following co-ordinates: A: x = 0 seconds; y = 0 mol L-1
B: x = 8 seconds; y = 0.37 mol L-1
C: x = 15 seconds; y = 0.49 mol L-1
D: x = 23 seconds; y = 0.63 mol L-1
E: x = 30 seconds; y = 0.62 mol L-1
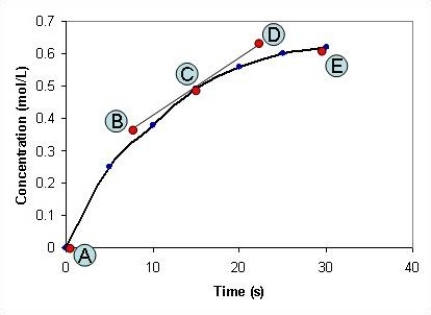 What is the rate of the chemical reaction after the reaction has been proceeding for fifteen seconds?
What is the rate of the chemical reaction after the reaction has been proceeding for fifteen seconds?
A) 3.26 mol L-1 s-1
B) 0.017 mol L-1 s-1
C) 0.021 mol L-1 s-1
D) 57.7 mol L-1 s-1
E) 48.39 mol L-1 s-1
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements is false when an enzyme is saturated?
A) The velocity of the reaction has reached Vmax
B) A further increase in substrate concentration leads to a decrease in velocity of the reaction.
C) The active site of every enzyme present is occupied.
D) The number of substrate molecules being processed by each enzyme molecule per second has reached the value of the enzyme's turnover number.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following graph depicts the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Which value, A-D, represents the Michaelis constant, KM, for the enzyme featured in the graph?
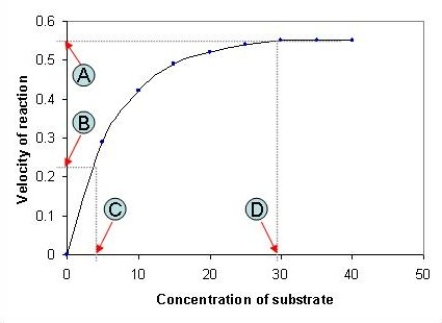
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of enzyme inhibition with the observed effect on Vmax and KM -Vmax decreases; KM decreases
A) Competitive inhibitor
B) Non-competitive inhibitor
C) Uncompetitive inhibitor
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the rate of a chemical reaction are true? Select all that apply.
A) The rate of a chemical reaction depends on the Gibbs free energy change of the reaction.
B) The rate of a reaction is given by calculating the change in concentration of a compound divided by the time.
C) The rate of a chemical reaction is constant for any particular reaction.
D) The rate of a chemical reaction varies with temperature.
E) The rate of a chemical reaction varies according to the reaction vessel used.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statement about enzymes is true?
A) Enzymes increase the rate of a chemical reaction by eliminating the activation energy.
B) Most enzymes are nucleic acids.
C) Enzymes can distinguish between enantiomers.
D) Enzymes are rarely specific for the reactions they catalyse.
E) Enzymes are rigidly fixed into a specific three-dimensional structure.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors affect the rate of a chemical reaction? Select all that apply.
A) The Gibbs free energy change of the reaction.
B) The temperature at which the reaction occurs.
C) The concentration of the reactants.
D) The presence of a catalyst.
E) The entropy change of reaction.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B,C,D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of enzyme inhibition with the observed effect on Vmax and KM -Vmax is unchanged; KM increases
A) Competitive inhibitor
B) Non-competitive inhibitor
C) Uncompetitive inhibitor
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of enzyme inhibition with the observed effect on Vmax and KM -Vmax decreases; KM is unchanged
A) Competitive inhibitor
B) Non-competitive inhibitor
C) Uncompetitive inhibitor
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Look at the graph below. At which time point, A-D, is the reaction at its slowest?
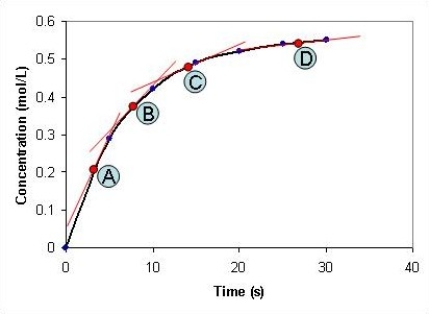
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the temperature of a reaction is increased, the rate of the reaction is also increased. Which of the following is the correct reason for this?
A) The Gibbs free energy of the reaction is lowered.
B) The activation energy is lowered.
C) The number of molecular collisions is increased.
D) The kinetic energy of the system is lowered.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The way in which the rate of a reaction depends on the concentration of its reactants is described by which of the following?
A) The free energy of the reaction
B) The rate constant
C) The order of the reaction
D) The half life of the reaction
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to function at maximum efficiency, enzymes often require which of the following? Select any that apply.
A) To be heated.
B) To be flexible.
C) To be in an environment with a particular pH.
D) To have an active site whose shape is complementary to the product(s) of the reaction.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning the action of a catalyst are true? Select all that apply.
A) Catalysts alter the enthalpy change of a reaction.
B) Catalysts are normally consumed during the course of a reaction.
C) Catalysts provide an alternative mechanism for the reaction.
D) Catalysts do not take part in the reaction that they speed up.
E) Catalysts lower the activation energy of a reaction.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The decomposition of a solution of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, was monitored over several days. Initially, hydrogen peroxide was present at a concentration of 1 mol L-1; after four days the hydrogen peroxide was present at a concentration of 0.5 mol L-1. What is the rate of the reaction for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide?
A) 1.40 10-6 mol L-1
B) 1.40 10-9 mol L-1 s-1
C) 1.40 10-6 mol L-1 s-1
D) 1.25 10-1 mol L-1 day-1
E) 8.68 10-5 mol L-1 min-1
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 20
Related Exams