A) initiation in eukaryotes
B) initiation in bacteria
C) elongation
D) termination
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not one of the modifications that can occur during the transition from a precursor mRNA to a mature RNA?
A) 3' polyadenylation
B) Removal of introns
C) Addition of a 5' guanine cap
D) Removal of sigma from the 5' end
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
DNA features are often represented using diagrams. Identify each feature on the following diagram.
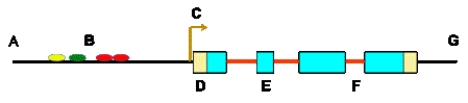
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the event with the transcription stage in which it occurs. -Sigma recruits RNA polymerase
A) initiation in eukaryotes
B) initiation in bacteria
C) elongation
D) termination
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of RNA with its function -Negative regulation
A) Carries information for amino acid sequence
B) Interprets nucleic acid information into amino acid information
C) Protein synthesis
D) Chromosome inactivation
E) Splicing
F) Negative regulation
G) Regulation of cellular processes
I) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of RNA with its function -Protein synthesis
A) Carries information for amino acid sequence
B) Interprets nucleic acid information into amino acid information
C) Protein synthesis
D) Chromosome inactivation
E) Splicing
F) Negative regulation
G) Regulation of cellular processes
I) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are true about transcription elongation? Please select all that apply.
A) Multiple genes can be co-transcribed
B) Multiple RNA polymerase molecules can act on a gene at the same time.
C) Transcripts are usually proofread
D) Bacterial elongation is sigma-dependent
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of RNA with its function -Splicing
A) Carries information for amino acid sequence
B) Interprets nucleic acid information into amino acid information
C) Protein synthesis
D) Chromosome inactivation
E) Splicing
F) Negative regulation
G) Regulation of cellular processes
I) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the eukaryotic RNA polymerase with the type of RNA it transcribes. -rRNA
A) RNAPI
B) RNAPII
C) RNAPIII
D) RNAPIV
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Epigenetic changes are heritable
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about transcription factors are false? Please select all that apply.
A) Each transcription factor is specific to one gene
B) A transcription factor binds to all instances of its recognition sequence
C) Each gene is controlled by multiple transcription factors
D) Binding sites are not known for all human transcription factors.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the eukaryotic RNA polymerase with the type of RNA it transcribes. -siRNA
A) RNAPI
B) RNAPII
C) RNAPIII
D) RNAPIV
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a reporter gene?
A) A gene that is regulated by a reporter sequence
B) A gene that encodes a reporter enhancer
C) A regulatory sequence that controls a fluorescent protein or other visual marker
D) A gene that is used to investigate promoter activity
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are components of the preinitiation complex? Please select all that apply.
A) General transcription factors
B) RNA polymerase
C) Initiator elements
D) Exons
E) TFIID
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
If binding of one transcription factor increases the likelihood that another transcription factor will bind, this is termed _____ binding
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about splicing are true? Please select all that apply.
A) Alternative splicing is rare in mammals
B) Introns in bacteria are smaller than in eukaryotes
C) The spliceosome uses base complementarity to recognize the splice site.
D) Splicing rearranges exons and the amino acid sequence cannot therefore be predicted from the gene sequence.
E) Alternative splicing allows multiple mature mRNAs to be produced from the same gene.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true of histone modifications?
A) Modifications are on the N-terminal histone tail
B) Modifications often occur on lysine residues
C) Methylation is usually associated with chromatin that is closed to transcription
D) Serine residues can be phosphorylated
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of RNA with its function -Carries information for amino acid sequence
A) Carries information for amino acid sequence
B) Interprets nucleic acid information into amino acid information
C) Protein synthesis
D) Chromosome inactivation
E) Splicing
F) Negative regulation
G) Regulation of cellular processes
I) F) and G)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of RNA with its function -Regulation of cellular processes
A) Carries information for amino acid sequence
B) Interprets nucleic acid information into amino acid information
C) Protein synthesis
D) Chromosome inactivation
E) Splicing
F) Negative regulation
G) Regulation of cellular processes
I) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Match the missing words in the following phrase. Transcription factors cluster together at the [A], which integrates inputs from multiple transcription factors. Binding sites that are involved in activating gene expression are [B]. Binding sites are [C] and transcription factors are [D]. Components of a gene are [E] and can be exchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 37
Related Exams