A) UGG
B) GUG
C) GUA
D) UUC
E) CAU
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the 1920s, Muller discovered that X-rays caused mutation in Drosophila. In a related series of experiments in the 1940s, Charlotte Auerbach discovered that chemicals-she used nitrogen mustards-have a similar effect. A new chemical food additive is developed by a cereal manufacturer. Why do we test for its ability to induce mutation?
A) We worry that it might cause mutation in cereal grain plants.
B) We want to make sure that it does not emit radiation.
C) We want to be sure that it increases the rate of mutation sufficiently.
D) We want to prevent any increase in mutation frequency.
E) We worry about its ability to cause infection.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use this representation to answer the following questions. DNA template strand 5' ____________________________ 3' DNA complementary strand 3' ____________________________ 5' -Given the locally unwound double strand above, in which direction does the RNA polymerase move?
A) 3' → 5' along the template strand
B) 5' → 3' along the template strand
C) 3' → 5' along the complementary strand
D) 5' → 3' along the complementary strand
E) 5' → 3' along the double-stranded DNA
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following model of a eukaryotic transcript to answer the next few questions. 5' UTR E₁ I₁ E₂ I₂ E₃ I₃ E₄ UTR 3' -Which of the following is a useful feature of introns for this model?
A) They are translated into small polypeptides.
B) They become parts of snRNPs.
C) Each intron has enzymatic properties.
D) Introns allow exon shuffling.
E) Introns protect exon structure.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which small-scale mutation would be most likely to have a catastrophic effect on the functioning of a protein?
A) a base substitution
B) a base deletion near the start of a gene
C) a base deletion near the end of the coding sequence, but not in the terminator codon
D) deletion of three bases near the start of the coding sequence, but not in the initiator codon
E) a base insertion near the end of the coding sequence, but not in the terminator codon
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Changes in a single nucleotide pair within a gene is called
A) substitution.
B) translocation.
C) point mutation.
D) silent mutation.
E) evolution.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of mutation, resulting in an error in the mRNA just after the AUG start of translation, is likely to have the most serious effect on the polypeptide product?
A) a deletion of a codon
B) a deletion of two nucleotides
C) a substitution of the third nucleotide in an ACC codon
D) a substitution of the first nucleotide of a GGG codon
E) an insertion of a codon
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to this figure of a simple metabolic pathway:
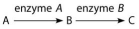 -If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain that is mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme A would be able to grow on which of the following media?
-If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain that is mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme A would be able to grow on which of the following media?
A) minimal medium
B) minimal medium supplemented with nutrient A only
C) minimal medium supplemented with nutrient B only
D) minimal medium supplemented with nutrient C only
E) minimal medium supplemented with nutrients A and C
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Yeast is capable of synthesizing the amino acids necessary for survival and can grow on minimal media or enriched media easily. In both conditions, the colonies have a cream colour. The production of adenine is regulated by two genes, ADE1 and ADE2. If either of these genes is defective, adenine cannot be synthesized and the colony will look red (as a result of accumulation of precursors) . A common undergraduate lab study is to irradiate yeast cells with ultra violet light from 2-5 sec up to 1-5 minutes, and see what will happen. -If, after irradiating and growing cultures in enriched media, you see some red colonies, what is the easiest way to confirm that the phenotype observed is due to a lack of adenine metabolism?
A) Grow them with and without adenine in the media.
B) Grow them with and without the adenine precursor.
C) You would have to see the DNA sequences.
D) Look for the protein products and compare them to wild type.
E) See if the colonies could survive with a higher dosage of UV irradiation.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to this figure of a simple metabolic pathway:
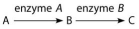 -A mutation results in a defective enzyme A. Which of the following would be a consequence of that mutation?
-A mutation results in a defective enzyme A. Which of the following would be a consequence of that mutation?
A) an accumulation of A and no production of B and C
B) an accumulation of A and B and no production of C
C) an accumulation of B and no production of A and C
D) an accumulation of B and C and no production of A
E) an accumulation of C and no production of A and B
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to this figure of a simple metabolic pathway:
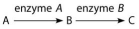 -According to Beadle and Tatum"s hypothesis, how many genes are necessary for this pathway?
-According to Beadle and Tatum"s hypothesis, how many genes are necessary for this pathway?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) It cannot be determined from the pathway.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
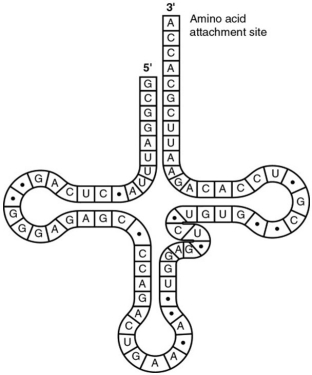 -The tRNA shown in the figure has its 3' end projecting beyond its 5' end. What will occur at this 3' end?
-The tRNA shown in the figure has its 3' end projecting beyond its 5' end. What will occur at this 3' end?
A) The codon and anticodon complement one another.
B) The amino acid binds covalently.
C) The excess nucleotides (ACCA) will be cleaved off at the ribosome.
D) The small and large subunits of the ribosome will attach to it.
E) The 5' cap of the mRNA will become covalently bound.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During splicing, which molecular component of the spliceosome catalyzes the excision reaction?
A) protein
B) DNA
C) RNA
D) lipid
E) sugar
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Garrod's information about the enzyme alteration resulting in alkaptonuria led to further elucidation of the same pathway in humans. Phenylketonuria (PKU) occurs when another enzyme in the pathway is altered or missing, resulting in a failure of phenylalanine (phe) to be metabolized to another amino acid: tyrosine. Tyrosine is an earlier substrate in the pathway altered in alkaptonuria. How might PKU affect the presence or absence of alkaptonuria?
A) It would have no effect, because PKU occurs several steps away in the pathway.
B) It would have no effect, because tyrosine is also available from the diet.
C) Anyone with PKU must also have alkaptonuria.
D) Anyone with PKU is born with a predisposition to later alkaptonuria.
E) Anyone with PKU has mild symptoms of alkaptonuria.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular triplet of bases in the coding sequence of DNA is AAA. The anticodon on the tRNA that binds the mRNA codon is
A) TTT.
B) UUA.
C) UUU.
D) AAA.
E) either UAA or TAA, depending on first base wobble.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not occur in prokaryotic eukaryotic gene expression, but does in eukaryotic gene expression?
A) mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are transcribed.
B) RNA polymerase binds to the promoter.
C) A poly-A tail is added to the 3' end of an mRNA and a cap is added to the 5' end.
D) Transcription can begin as soon as translation has begun even a little.
E) RNA polymerase requires a primer to elongate the molecule.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular triplet of bases in the template strand of DNA is 5' AGT 3'. The corresponding codon for the mRNA transcribed is
A) 3' UCA 5'.
B) 3' UGA 5'.
C) 5' TCA 3'.
D) 3' ACU 5'.
E) either UCA or TCA, depending on wobble in the first base.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a nucleotide substitution switched a U for a C, such that the codon was read as CGC instead of CGU, what would the effect be?
A) a misfolding of the protein
B) an incomplete protein
C) nothing, as the third nucleotide does not determine the amino acid used.
D) nothing, since both these codons code for arginine
E) it would initiate a tumour
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A transcription unit that is 8000 nucleotides long may use 1200 nucleotides to make a protein consisting of approximately 400 amino acids. This is best explained by the fact that
A) many noncoding stretches of nucleotides are present in mRNA.
B) there is redundancy and ambiguity in the genetic code.
C) many nucleotides are needed to code for each amino acid.
D) nucleotides break off and are lost during the transcription process.
E) there are termination exons near the beginning of mRNA.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that exposure to a chemical mutagen results in a change in the sequence that alters the 5' end of intron 1 (I₁) . What might occur?
A) loss of the gene product
B) loss of E₁
C) premature stop to the mRNA
D) inclusion of I₁ in the mRNA
E) exclusion of E₂
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 91
Related Exams