A) meniscus
B) bursa
C) articular cartilage
D) synovial membrane
E) joint cavity
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Why is the inferior region of the shoulder joint most vulnerable to dislocation?
Correct Answer

verified
The anterior,superior,and posterior surf...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
You ________ your mandible when you grasp your upper lip with your lower teeth.
A) rotate
B) extend
C) pivot
D) protract
E) pronate
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following movements is a good example of supination?
A) opening the mouth
B) turning the hand palm upward
C) extreme bending of the head backwards
D) moving the hand toward the shoulder
E) spreading the fingers
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ligament that provides support to the front of the knee joint is the ________ ligament.
A) anterior cruciate
B) posterior cruciate
C) patellar
D) popliteal
E) tibial collateral
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hip joint can also be referred to as the ________ joint.
A) coccygeal
B) coxal
C) condyloid
D) sacroiliac
E) ellipsoid
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
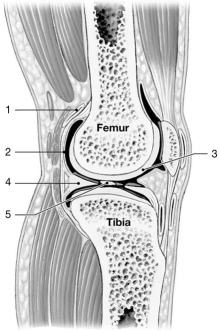 Figure 9-1 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "2."
Figure 9-1 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "2."
A) serous membrane
B) synovial membrane
C) joint capsule
D) periosteum
E) intracapsular ligament
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The surface of articular cartilage is
A) slick.
B) flat.
C) smooth.
D) rough.
E) both slick and smooth.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The coxal bones articulate with the sacrum at the ________ joint.
A) vertebrocoxal
B) coxosacral
C) iliocoxal
D) vertebroilial
E) sacroiliac
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The movement of a body part upward is called
A) extension.
B) protraction.
C) supination.
D) elevation.
E) abduction.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The shoulder joint,or ________ joint,permits the greatest range of motion of any joint.
A) coracocondylar
B) humeroacromial
C) clavicoscapular
D) glenohumeral
E) deltobrachial
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Muscles that extend the elbow attach to the
A) coronoid process.
B) radial tuberosity.
C) olecranon process.
D) medial epicondyle.
E) lateral epicondyle.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three functions of synovial fluid are nutrient distribution,shock absorption,and
A) stabilization.
B) lubrication.
C) padding.
D) strengthening.
E) enzyme secretion.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The knee joint is stabilized by ________ major ligaments.
A) 3
B) 5
C) 7
D) 9
E) 11
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following movements is a good example of flexion?
A) opening the mouth
B) turning the hand palm upward
C) extreme bending of the head backwards
D) moving the hand toward the shoulder
E) spreading the fingers
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dense fibrous connective tissue is to a suture as a periodontal ligament is to a(n)
A) amphiarthrosis.
B) syndesmosis.
C) synostosis.
D) synchondrosis.
E) gomphosis.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A herniated intervertebral disc is caused by
A) loss of annulus fibrosis elasticity.
B) slippage of the fibrocartilage disc.
C) ossification of the vertebral disc.
D) protrusion of the nucleus pulposus.
E) transformation of fibrocartilage to hyaline cartilage.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following joints is an example of a ball-and-socket joint?
A) elbow
B) knee
C) ankle
D) wrist
E) shoulder
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ligament that encloses the ________ attaches to the tibial tuberosity.
A) head of the femur
B) greater trochanter
C) medial malleolus
D) lesser trochanter
E) patella
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is one of the four major types of synarthrotic joints?
A) suture
B) gomphosis
C) synchondrosis
D) synostosis
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 127
Related Exams