A) a loan that a borrower is required to hold on deposit at a correspondent bank.
B) a loan that a borrower is required to hold on deposit in foreign reserves.
C) a loan that a borrower is required to hold on deposit at the lending institution.
D) the investment that a borrower is required to hold on deposit at the lending institution.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term disintermediation refers to the process in which firms access:
A) money markets directly.
B) money markets via financial intermediaries.
C) capital markets directly.
D) capital markets via financial intermediaries.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The key factors entering into the credit decision include:
A) borrower-specific factors that are idiosyncratic to the individual borrower.
B) market-specific factors that have an impact on all borrowers at the time of the credit decision.
C) global-economic factors that have an impact on all FI's at the time of credit decision.
D) borrower-specific factors that are idiosyncratic to the individual borrower and market-specific factors that have an impact on all borrowers at the time of the credit decision.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Explain the major concept of Altman's linear discriminant model. What would you consider to be the major disadvantages of this model?
Correct Answer

verified
Discriminant models divide borrowers into high or low default risk classes contingent on their observed characteristics (Xj). Similar to linear probability models, linear discriminant models use past data as inputs into a model to explain repayment experience on old loans. The relative importance of the factors used in explaining past repayment performance then forecasts whether the loan falls into the high or low default class.
In Altman's linear discriminant model, the indicator variable Z is the overall measure of the default risk classification of a borrower.This in turn depends on the values of various financial ratios of the borrower (Xj) and the weighted importance of these ratios based on the past observed experience of defaulting versus non-defaulting borrowers derived from a discriminant analysis model. According to Altman's credit scoring model, a score of less than 1.81 would place the potential borrower into a high default risk category. Any score above 2.99 is regarded as a low default risk, while a score between 1.81 and 2.99 is in the 'zone of ignorance', where a borrower may or may not default.
Several criticisms have been levied against linear discriminant models. First, the models identify only two extreme categories of risk: default or no default. The real world considers several categories of default severity. Second, the relative weights of the variables may change over time. Further, the actual variables to be included in the model may change over time. Third, these models ignore important, hard-to-quantify factors that may play a crucial role in the default or no default decision. For example, the reputation of the borrower and the nature of long-term borrower-lender relationships could be important borrower-specific characteristics, as could macroeconomic factors, such as the phase of the business cycle. Fourth, no centralised database on defaulted business loans for proprietary and other reasons exists. This constrains the ability of many FIs to use traditional credit scoring models (and quantitative models in general) for larger business loans.
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following data of a prospective borrower. 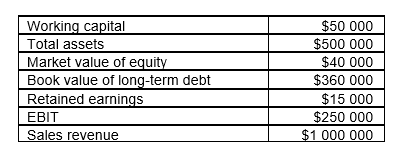 What is this company's Z score (round to two decimals) ?
What is this company's Z score (round to two decimals) ?
A) 3.78
B) 3.88
C) 3.98
D) 4.08
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
By selecting and combining different economic and financial borrower characteristics, an FI manager may be able to improve the pricing of default risk.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following formula for calculating the contractually promised gross return on a loan k, per dollar lent: (1 + k) = 1 + [f + (BR + m) ]/ {1 - [b(1 - R) ]}. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The denominator is the promised gross cash inflow to the FI per dollar.
B) The denominator reflects direct fees plus the loan interest rate consisting of both, the base lending rate and the credit risk premium.
C) The formula ignores present value aspects.
D) The FI's net benefit from requiring compensating balances must consider the benefits of holding additional non-interest bearing reserve requirements.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Term structure of credit risk approach models are also known as:
A) reduced-form models.
B) mortality rate models.
C) RAROC models.
D) structural models.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A loan provided by a group of FIs as opposed to a single lender is called:
A) a joint loan.
B) project finance.
C) a syndicated loan.
D) a multiple loan.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Moody's KMV Credit Monitor Model compares loans with the pay-off functions of swaps.
B) Moody's KMV Credit Monitor Model uses rating migrations data to calculate hypothetical loan values.
C) Moody's KMV Credit Monitor Model discriminates between two types of borrowers, i.e. borrowers that are likely to default and borrowers that are unlikely to default.
D) None of the listed options are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) A commercial paper is an unsecured long-term debt instrument issued by corporations.
B) A commercial paper is a secured long-term debt instrument issued by corporations.
C) A commercial paper is a secured short-term debt instrument issued by corporations.
D) A commercial paper is an unsecured short-term debt instrument issued by corporations.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that i1 = 11 per cent and i2 = 12 per cent, and that k1 = 14.50 per cent and k2 = 16.50 per cent. What is the expected probability of repayment on the one-year corporate bonds in one year's time (round to two decimals) ?
A) 86.99 per cent
B) 81.47 per cent
C) 86.50 per cent
D) 95.34 per cent
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Default risk is the risk that the borrower is willing but unable to fulfil the terms promised under loan contract.
B) Default risk is the risk that the borrower refinances the loan before maturity.
C) Default risk is the risk that the borrower is able but unwilling to fulfil the terms promised under loan contract.
D) Default risk is the risk that the borrower is unable and unwilling to fulfil the terms promised under loan contract.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the context of the KMV Credit Monitor Model, the market value of a risky loan made by a lender to a borrower can be expressed as:
A) F(r) = Be-i/r[(1/d) N(h1) + N(h2) ]
B) F(r) = Be-ir[(1/d) N(h1) + N(h2) ]
C) F(r) = Be-ir[(1/d) - N(h1) + N(h2) ]
D) F(r) = Be-ir[(1/d) N(h1) N(h2) ]
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An unsecured loan is also referred to as:
A) non-asset backed loan.
B) mezzanine debt.
C) junior debt.
D) senior debt.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A borrower's leverage refers to the payment capacity, that is, the 'leverage' the borrower has to service its loans.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Banks have been partially responsible for big corporate collapses such as Enron.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Borrower-specific factors are factors that affect all borrowers operating in the same industry.
B) Market-specific factors are factors that are idiosyncratic factors arising from the market that affect s single or a small number of borrowers.
C) Market-specific factors carry a higher weight compared to borrower-specific factors when deciding on whether to accept or to reject a loan application.
D) None of the listed options are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Moody's KMV Credit Monitor Model compares loans with option payoffs.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the interest rate in the market for one-year zero-coupon government bonds is i = 8 per cent and the rate for one-year zero-coupon grade BBB bonds is k = 10.2 per cent. What is the implied probability of repayment on the corporate bond (round to two decimals) ?
A) 2.00 per cent
B) 2.04 per cent
C) 97.96 per cent
D) 98.00 per cent
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 65
Related Exams