A) indicates consumption spending beyond current income.
B) implies the household is paying above-market prices for the goods in question.
C) implies the household is paying below-market prices for the goods in question.
D) implies that the household is not spending all of its income on the goods in question.
E) shows a combination of goods that are beyond the income of the household.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diagrams A,B,and C show 3 individual consumers' demand curves for cement.Consumers A,B,and C constitute the entire monthly cement market in this region. 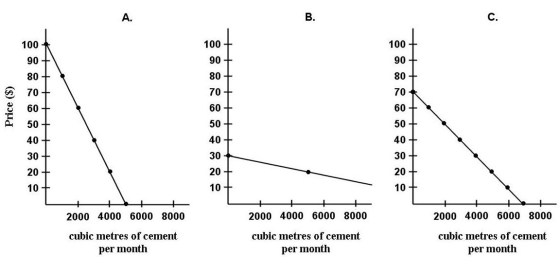 FIGURE 6-3
-Refer to Figure 6-3.What is the market demand (in cubic metres per month) for cement at a price of $60 per cubic metre?
FIGURE 6-3
-Refer to Figure 6-3.What is the market demand (in cubic metres per month) for cement at a price of $60 per cubic metre?
A) 0
B) 1000
C) 2000
D) 3000
E) 4000
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Indifference theory is based on the assumption that
A) consumers are not able to rank consumption bundles in order of preference.
B) consumers can always say which of two consumption bundles they prefer without having to say by how much they prefer it.
C) the consumer has equated the marginal utilities of all products,and is therefore indifferent between consumption bundles.
D) the consumer is able to quantify the difference in total utility received from two different consumption bundles.
E) the consumer receives the same utility and is therefore indifferent between any two consumption bundles.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In economics,the term "utility" is defined as the
A) system of basing the price of a good on its usefulness to society.
B) usefulness of a good.
C) total consumer satisfaction received from consumption of a good.
D) usefulness of a theory to explain price determination.
E) a service such as sewer and water or electricity.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A basic hypothesis of marginal utility theory is that the utility a consumer derives from successive units of a good diminishes as total consumption of the good increases.This hypothesis is known as
A) the paradox of value.
B) the utility theory of demand.
C) utility maximization.
D) the law of diminishing marginal utility.
E) the law of diminishing total utility.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume an individual with a downward-sloping demand curve is paying a single price for each unit of some commodity.He will experience consumer surplus on
A) all units that were not bought at that particular price.
B) all of the units bought.
C) all units bought with the possible exception of the last unit.
D) the first unit only.
E) none of the units.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the substitution and income effects of a 15% increase in the price of a good.Of the goods listed below,which is most likely to have the largest income effect?
A) salt
B) paperclips
C) socks
D) tennis balls
E) electricity
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
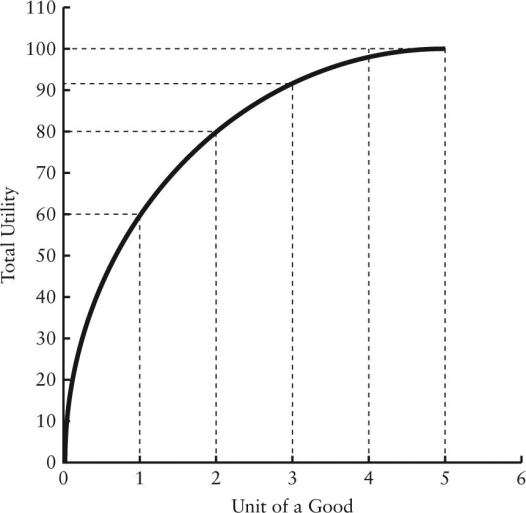 FIGURE 6-1
-Refer to Figure 6-1.Total utility is at its maximum when marginal utility is
FIGURE 6-1
-Refer to Figure 6-1.Total utility is at its maximum when marginal utility is
A) equal to zero.
B) negative.
C) positive.
D) equal to total utility.
E) at the maximum.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The total value that Doug places on his consumption of computer games equals
A) the price multiplied by quantity demanded.
B) his marginal utility multiplied by quantity demanded.
C) price times marginal value.
D) the total amount he pays for all the games he purchases.
E) his total expenditure on computer games plus his consumer surplus.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
6A-4 Deriving the Demand Curve -Refer to Figure 6-9.In part (ii) ,the line joining points X,Y,and Z is known as ________,which shows how ________.
A) a price-consumption line; consumption changes as relative prices change,with money income constant
B) an income-consumption line; consumption changes as income changes,with relative prices held constant
C) a price-consumption line; consumption changes as money income and relative prices change
D) an income-consumption line; consumption changes with changing relative prices and constant income
E) an indifference map; the value of various combinations of two goods changes
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal utility analysis predicts a downward-sloping demand curve for good X because
A) as PX falls,the ratio MUX/PX becomes smaller,causing the consumer to purchase more of good X.
B) as PX rises,the consumer increases purchases of X such that MUX/PX is equal to MU/P for all other products.
C) utility-maximizing consumers equate marginal utility received for each product consumed.
D) all demand curves are downward sloping,regardless of the behaviour of consumers.
E) as PX falls,the consumer increases purchases of X until MUX/PX is equal to MU/P for all other products.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there are only two goods,A and B,and that consumer income is constant.If the price of good A falls and the consumption of good B rises,we can conclude that
A) A is a normal good.
B) B is a normal good.
C) A is an inferior good.
D) B is an inferior good.
E) both A and B are normal goods.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal rate of substitution measures the tradeoff between the
A) prices of two goods along a budget line.
B) different values that two consumers place on a good.
C) amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another good along an indifference curve.
D) different indifference curves.
E) amount of one good the consumer is willing to purchase and its own price.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Smith family is allocating its monthly household expenditure between only two goods,food and clothing.Suppose that the price of food is $5 per unit,and the price of clothing is $10 per unit and that the marginal utility that the family is receiving from its consumption of food is currently 25.What is the family's marginal utility from its consumption of clothing if it is maximizing its utility?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 12.5
D) 25
E) 50
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Christine is allocating her household expenditure between cleaning services and gardening services in order to maximize the household's total utility.For the quantities of cleaning and gardening services she has chosen,an increase in the price of cleaning service will,ceteris paribus,
A) increase the marginal utility of a unit of cleaning service.
B) reduce the marginal utility per dollar spent on cleaning service.
C) reduce the marginal utility of a unit of cleaning service.
D) increase the marginal utility per dollar spent on cleaning service.
E) have no effect on the marginal utility per dollar spent on cleaning service.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
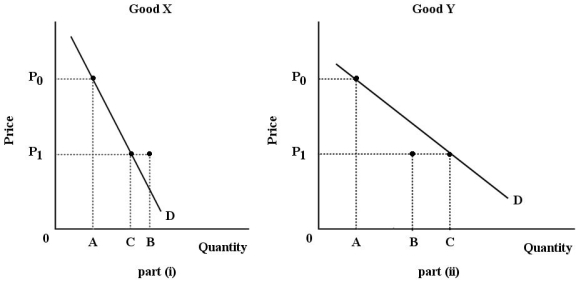 FIGURE 6-4
-Refer to Figure 6-4.For both goods,the price falls from P0 to P1.The substitution effect is illustrated by the change in quantity demanded from A to B; the income effect is illustrated by the change in quantity demanded from B to C.Good Y is certainly a(n) ________ good.
FIGURE 6-4
-Refer to Figure 6-4.For both goods,the price falls from P0 to P1.The substitution effect is illustrated by the change in quantity demanded from A to B; the income effect is illustrated by the change in quantity demanded from B to C.Good Y is certainly a(n) ________ good.
A) normal
B) inferior
C) luxury
D) necessity
E) Giffen
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
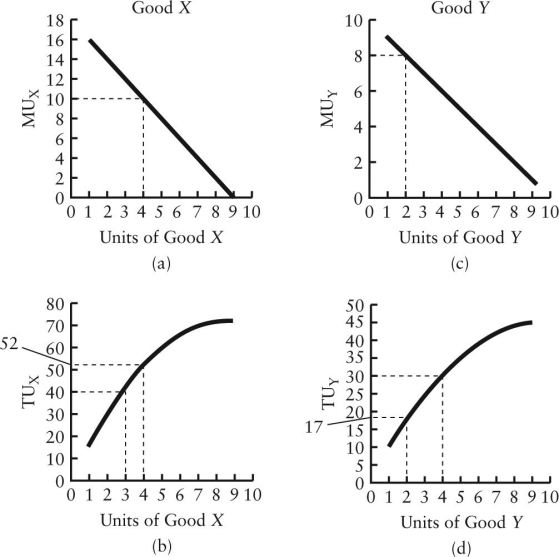 FIGURE 6-2
-Refer to Figure 6-2.Suppose that the price of X is $2,the price of Y is $1,and the consumer's income is $10.The consumer is currently buying 3 units of good X and 4 units of good Y.In order to maximize his/her utility,the consumer should
FIGURE 6-2
-Refer to Figure 6-2.Suppose that the price of X is $2,the price of Y is $1,and the consumer's income is $10.The consumer is currently buying 3 units of good X and 4 units of good Y.In order to maximize his/her utility,the consumer should
A) not change his/her behaviour.
B) buy the same amount of X but less Y.
C) buy more of X but the same amount Y.
D) buy more of X and less Y.
E) buy less of X and more Y.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The idea that the utility a consumer derives from successive units of a good diminishes as total consumption of the good increases is known as
A) the paradox of value.
B) the utility theory of demand.
C) utility maximization.
D) diminishing marginal utility.
E) diminishing total utility.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since there is a limited supply of diamonds in the world,the consumption of diamonds
A) takes place at relatively low marginal value.
B) takes priority over some other good.
C) is no less important than consumption of water.
D) takes place at relatively high marginal value.
E) should be regulated by the government.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following situations will an individual's purchasing power be unaffected?
A) money income doubles and the prices of all goods and services are cut in half
B) money income remains constant and the prices of all goods and services double
C) money income is cut in half and the prices of all goods and services double
D) money income is cut in half and the prices of all goods and services remains constant
E) money income doubles and the prices of all goods and services double
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 140
Related Exams