A) a demand curve.
B) a price constraint.
C) a break-even point.
D) a supply curve.
E) a marginal revenue curve.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Factors that limit the range of prices a firm may set are referred to as
A) pricing restraints.
B) pricing constraints.
C) demand factors.
D) pricing barriers.
E) pricing restrictions.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Insurance premiums,entrance fees,train fares,and organization dues are all examples of
A) premiums.
B) barter.
C) profit.
D) price.
E) outlays.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The manufacturer of a new kind of fat-free ice cream that has the consistency and taste of regular ice cream is thinking of using a penetration pricing strategy for its new product.Which of the following conditions would argue against using a penetration pricing strategy for the tasty,fat-free ice cream?
A) The ice cream market is highly elastic.
B) A large portion of the market has inelastic demand for ice cream over a broad range of prices.
C) Economies of scale in production would be substantial.
D) Retailers are not willing to pay for new brands of premium ice cream in the already overcrowded category.
E) Once the initial price is set, it is nearly impossible to lower prices without alienating buyers.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This is an example of a __________ strategy.
A) penetration pricing
B) target pricing
C) bundle pricing
D) loss-leader pricing
E) prestige pricing
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determining cost,volume,and profit relationships would occur during which stage of the price-setting process?
A) Defining the scope of the product
B) Selecting an approximate price level
C) Setting the list or quoted price
D) Evaluating the success of the price strategy
E) Making special adjustments to the list price
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-2 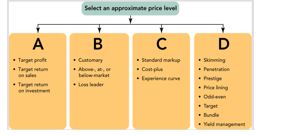 -Figure 11-2 represents the four approaches to selecting an appropriate price level.Box D includes customary and loss leader so it represents which approach?
-Figure 11-2 represents the four approaches to selecting an appropriate price level.Box D includes customary and loss leader so it represents which approach?
A) competition-oriented approach
B) cost-oriented approach
C) profit-oriented approach
D) results-oriented approach
E) demand-oriented approach
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pricing objectives involve
A) reconciling the prices charged by an organization to the values set forth in its business mission.
B) taking specific steps to capitalize on an organization's internal strengths as they apply to price.
C) specifying the role of price in an organization's marketing and strategic plans.
D) taking specific steps to compensate for an organization's weaknesses as they apply to price.
E) subjectively setting intrinsic values to all products and services offered by an organization.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the iPad's __________ stage of its product life cycle,Apple had great latitude in setting a price for the product because of a lack of competition.
A) decline
B) maturity
C) growth
D) accelerated development
E) introduction
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm's profit objective is often measured in terms of ROI.The acronym ROI stands for
A) risk opportunity investment.
B) revised organizational incentives.
C) return on investment.
D) regulated organizational investments.
E) replenishment of organizational inventories.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mark Johnson,the manager of a discount consumer electronics store,was approached by the manufacturer's representative on behalf of a marketer of a popular and profitable line of storage racks.The manufacturer's representative implied that if Johnson didn't raise the retail prices for the storage racks to those paid by the marketer's non-discount customers,Johnson's supply of racks may be severely curtailed.The manufacturer's representative was guilty of attempting
A) horizontal price-fixing.
B) vertical price-fixing.
C) price discrimination.
D) predatory pricing.
E) bait and switch pricing.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A conspiracy among firms to set prices for a product is referred to as
A) price discrimination.
B) price fixing.
C) predatory pricing.
D) tying arrangements.
E) exclusive dealing.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Yield management is considered to be a __________ approach to pricing.
A) demand-oriented
B) cost-oriented
C) profit-oriented
D) competition-oriented
E) service-oriented
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prestige pricing is considered to be a __________ approach to pricing.
A) demand-oriented
B) cost-oriented
C) profit-oriented
D) competition-oriented
E) service-oriented
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a cost-oriented pricing method?
A) loss-leader pricing
B) standard markup pricing
C) at-, above-, or below-market pricing
D) price lining
E) penetration pricing
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Southern gardeners normally pay $5 for a two-cubic-foot bag of pine bark mulch that they buy at their local gardening-supply and home-improvement stores to keep the weeds down in their gardens.If the price being charged by a retailer is not within a narrow range that gardeners feel is appropriate,they will use substitutions-newspaper,grass clippings,or some other kind of covering.When pricing pine bark mulch,a garden-supply or home-improvement retailer should use
A) customary pricing.
B) at-market pricing.
C) loss-leader pricing.
D) penetration pricing.
E) bundle pricing.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Setting one price for all buyers of a product or service is referred to as
A) customary pricing.
B) a one-price policy.
C) a dynamic pricing policy.
D) standard markup pricing.
E) uniform pricing.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Setting a price to achieve a profit that is a specified percentage of the sales volume is referred to as
A) target return-on-investment pricing.
B) target return-on-sales pricing.
C) loss-leader pricing.
D) target pricing.
E) standard markup pricing.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Odd-even pricing is considered to be a __________ approach to pricing.
A) cost-oriented
B) profit-oriented
C) demand-oriented
D) competition-oriented
E) service-oriented
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a demand-oriented approach to pricing?
A) customary pricing
B) target profit pricing
C) standard markup pricing
D) bundle pricing
E) service-oriented pricing
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 374
Related Exams