A) parietal and frontal lobes.
B) occipital and parietal lobes.
C) temporal and occipital lobes.
D) parietal,occipital,and frontal lobes.
E) parietal,occipital,and temporal lobes.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a function of the blood-brain barrier?
A) It prevents nicotine and alcohol from entering brain interstitial fluid.
B) It prevents brain neurons from being exposed to drugs.
C) It prevents brain neurons from being exposed to waste products in the blood.
D) It protects brain neurons from exposure to abnormal hormone levels.
E) It protects brain neurons from exposure to abnormal ion levels.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the five secondary vesicles in the correct anterior to posterior order. A: Diencephalon B: Myelencephalon C: Telencephalon D: Metencephalon E: Mesencephalon
A) b,a,c,d,e
B) a,b,c,d,e
C) b,c,a,e,d
D) c,d,e,a,b
E) c,a,e,d,b
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This nucleus participates in the expression of emotions,control of behavior,and development of moods.
A) Amygdaloid body
B) Caudate nucleus
C) Putamen
D) Globus pallidus
E) Claustrum
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The superior cerebellar peduncles connect the pons to the cerebellum.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The portion of the adult brain that includes the cerebrum is derived from which secondary brain vesicle?
A) Telencephalon
B) Diencephalon
C) Myelencephalon
D) Metencephalon
E) Mesencephalon
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary somatosensory cortex is part of the
A) occipital lobe.
B) temporal lobe.
C) insula.
D) parietal lobe.
E) frontal lobe.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary gustatory cortex is part of the
A) occipital lobe.
B) temporal lobe.
C) insula.
D) parietal lobe.
E) frontal lobe.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dural venous sinuses are areas where
A) the meningeal and periosteal layers separate to form large blood-filled spaces.
B) cerebrospinal fluid is produced.
C) cerebrospinal fluid is stored.
D) large numbers of nuclei congregate.
E) glial cells are formed.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary motor cortex is part of the
A) occipital lobe.
B) temporal lobe.
C) insula.
D) parietal lobe.
E) frontal lobe.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This portion of the brain secretes the hormone melatonin,which helps to regulate the body's circadian rhythm.
A) Habenular nucleus
B) Anterior nucleus
C) Pineal gland
D) Mammillary body
E) Paraventricular nucleus
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The blood-brain barrier is made up of
A) microglial extensions and capillary endothelial cells.
B) ependymal cells and venous blood vessels.
C) astrocyte perivascular feet and capillary endothelial cells.
D) astrocyte extensions and dural sinuses.
E) astrocyte perivascular feet and the falx cerebri.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This nucleus controls muscular movement at the subconscious level.
A) Amygdaloid body
B) Caudate nucleus
C) Putamen
D) Globus pallidus
E) Claustrum
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The infundibulum is attached to the
A) pons.
B) thalamus.
C) pineal gland.
D) pituitary gland.
E) epithalamus.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The major pathway of communication between the right and left hemisphere is/are the
A) cerebral gyri.
B) cerebral sulci.
C) longitudinal fissure.
D) hypothalamus.
E) corpus callosum.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hemisphere lateralization refers to the
A) difficulty in assigning a precise function to a specific region of the cortex.
B) generalization that both cerebral hemispheres receive their sensory information from and project motor commands to the opposite side of the body.
C) separation of the various lobes of the brain from each other.
D) crisscrossing of information between the two hemispheres.
E) functional differences between the right and left hemispheres.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cranial nerve responsible for movement of the medial rectus,superior rectus,inferior rectus and inferior oblique eye muscles is the __________ nerve.
A) oculomotor
B) trochlear
C) abducens
D) trigeminal
E) hypoglossal
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The brain ventricle located in the diencephalon is the _____ ventricle.
A) third
B) lateral
C) fourth
D) median
E) falx
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
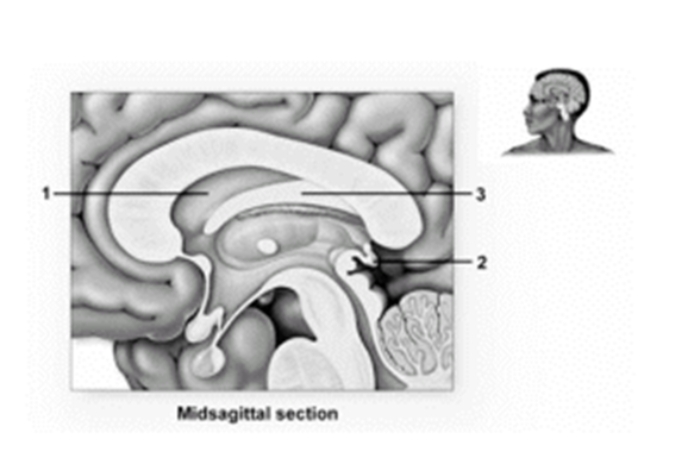 -This figure shows the diencephalon.What structure does number 1 indicate?
-This figure shows the diencephalon.What structure does number 1 indicate?
A) Corpus callosum
B) Septum pellucidum
C) Fornix
D) Thalamus
E) Pineal gland
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
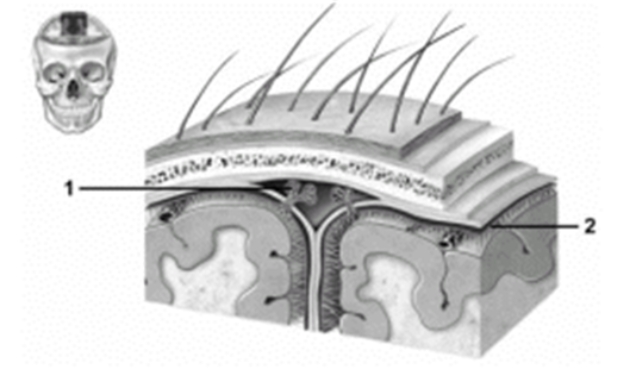 -This figure shows the cranial meninges.What structure does number 1 indicate?
-This figure shows the cranial meninges.What structure does number 1 indicate?
A) Pia mater
B) Arachnoid
C) Dura mater
D) Dural venous sinus
E) Arachnoid granulation
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 101
Related Exams