A) Global sources of money.
B) The time lag between when interest rates change and when investment changes.
C) How well individuals respond to the agricultural press releases.
D) Expectations about the economy in the future.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a series of events that accurately describes the steps by which restrictive monetary policy is effective?
A) Decrease in interest rate,decrease in M1,and increase in investment.
B) Decrease in M1,increase in interest rate,and decrease in investment.
C) Increase in M1,decrease in investment,and decrease in interest rate.
D) Increase in M1,increase in interest rate,and increase in investment.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary stimulus will fail if
A) Banks are reluctant to lend money.
B) The investment demand curve is fairly flat.
C) The money demand curve is fairly steep.
D) Consumers begin to spend more.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To reduce the level of unanticipated inflation,monetarists advocate
A) A sharp increase in short-term interest rates.
B) Steady and predictable changes in the money supply.
C) A decrease in short-term interest rates.
D) A decrease in government spending.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Currency held by the public,balances in transactions accounts,plus balances in most savings accounts and money market mutual funds are the
A) Money demand.
B) Federal funds.
C) Money supply (M1) .
D) Money supply (M2) .
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Bernanke's policy guide,a full-point decrease in long-term interest rates results in a
A) $10 billion stimulus for the economy.
B) $20 billion stimulus for the economy.
C) $200 billion stimulus for the economy.
D) $1,000 billion stimulus for the economy.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the money market is in equilibrium in the liquidity trap,
A) An increase in the money supply does not affect interest rates.
B) The demand for money is perfectly insensitive to interest rates.
C) Investment spending falls to zero.
D) There is no speculative demand for money.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In periods of restrictive monetary policy,which of the following industries are likely to feel a disproportionately large impact of the policy?
A) The auto industry.
B) Fast-food restaurants.
C) Cell phone service providers.
D) Soft drink companies such as Coke and Pepsi.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the economy is in the vertical portion of the aggregate supply curve,according to monetarists,an increase in the money supply in the long run will
A) Increase the price level.
B) Decrease the price level.
C) Increase the output level.
D) Decrease the output level.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary policy is most effective when the money demand curve is __________ and investment demand is _____________.
A) horizontal; elastic
B) downward-sloping; elastic
C) horizontal; inelastic
D) downward-sloping; inelastic
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The liquidity trap refers to the portion of the money demand curve that is
A) Upward-sloping.
B) Downward-sloping.
C) Horizontal.
D) Vertical.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the anticipated inflation rate is 5 percent and the nominal interest rate is 9 percent,the real interest rate will be
A) 4 percent.
B) Negative 14 percent.
C) 14 percent.
D) 5 percent.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the extreme monetarist position,using the equation of exchange,an increase in the quantity of money in circulation will
A) Increase real GDP.
B) Decrease the velocity of money.
C) Have no effect on the price level.
D) Increase the price level.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Fed could sell bonds in the open market in an effort to keep interest rates constant when
A) The discount rate increases.
B) Money demand increases.
C) The reserve requirement increases.
D) Money demand decreases.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Federal Reserve raises the discount rate,we would expect the
A) AS curve to increase.
B) Investment curve to increase.
C) AD curve to increase.
D) AD curve to decrease.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the monetarist view and the equation of exchange,which of the following will occur because the Fed sells securities in the open market?
A) A decrease in real interest rates.
B) A decrease in nominal aggregate spending.
C) A lower level of real output.
D) An increase in the price level.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
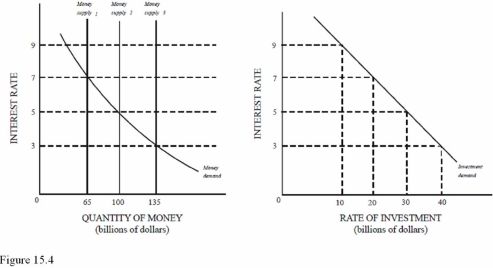 In Figure 15.4,a decrease in the money supply from $135 billion to $100 billion will cause all of the following except
In Figure 15.4,a decrease in the money supply from $135 billion to $100 billion will cause all of the following except
A) A $10 billion decrease in investment.
B) A decrease in the price level.
C) A decrease in aggregate demand.
D) An increase in borrowing.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary restraint is associated with all of the following except
A) A decrease in interest rates.
B) A decrease in the money supply.
C) An increase in the reserve requirement.
D) A decrease in aggregate demanD.Lower interest rates are associated with monetary stimulus.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assuming the aggregate supply curve is vertical,which of the following is most likely to occur if the Fed pursues expansionary monetary policy?
A) The equilibrium price level and output will both increase.
B) The equilibrium price level and output will both decrease.
C) The equilibrium price level will increase but output will stay the same.
D) The equilibrium output will increase but the price level will stay the same.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
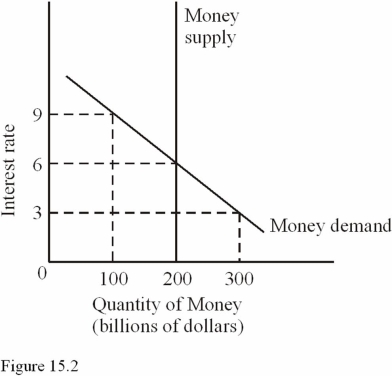 In Figure 15.2,if the money supply increased from $200 billion to $300 billion,all of the following would be likely to occur except
In Figure 15.2,if the money supply increased from $200 billion to $300 billion,all of the following would be likely to occur except
A) Interest rates would decline.
B) The quantity of money demanded would increase.
C) Aggregate demand would increase.
D) The money demand curve would shift to the right.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 150
Related Exams