A) The 1980s.
B) The Great Depression.
C) World War II.
D) The years following World War II.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
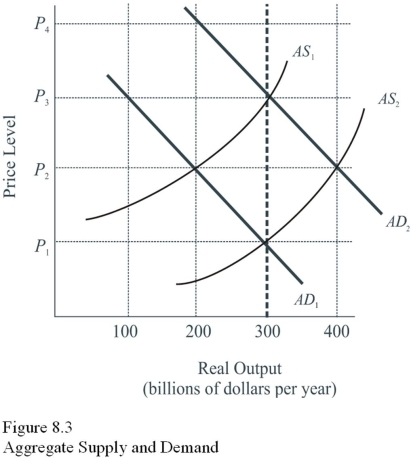 Assume the economy is initially in equilibrium on AD1 and AS1.Which curve would have shifted,and in what direction would it have shifted,if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of $300 billion and a price level of P3 in Figure 8.3?
Assume the economy is initially in equilibrium on AD1 and AS1.Which curve would have shifted,and in what direction would it have shifted,if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of $300 billion and a price level of P3 in Figure 8.3?
A) Aggregate supply would have shifted to the left.
B) Aggregate supply would have shifted to the right.
C) Aggregate demand would have shifted to the left.
D) Aggregate demand would have shifted to the right.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a potential problem at macro equilibrium?
A) It is inconsistent with the macroeconomic goals.
B) A surplus of goods exists.
C) A shortage of goods exists.
D) The economy is permanently stuck there.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Both Keynesian and monetarist theories emphasize the potential of aggregate demand shifts to alter macro outcomes. By altering spending,taxes,or the money supply,we can manipulate the AD curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
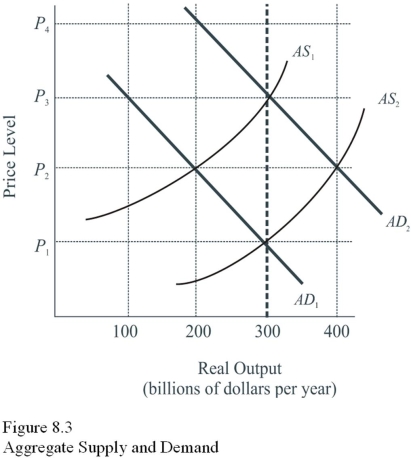 Given AD1 and AS1 in Figure 8.3,the Keynesian approach to achieving a higher level of output would be to
Given AD1 and AS1 in Figure 8.3,the Keynesian approach to achieving a higher level of output would be to
A) Impose price controls.
B) Increase the growth of the money supply to shift AS1 to AS2.
C) Do nothing.
D) Employ an expansionary fiscal policy.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The profit effect occurs because,in the short run,resource costs typically do not increase as rapidly as the price of goods and services. Some costs,like labor contracts or rents,do not immediately increase when the price level rises.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following situations is the percentage change in real GDP always positive?
A) Depression.
B) Inflation.
C) Recession.
D) Growth recession.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following can be used to measure macroeconomic performance except for the
A) Total real value of goods and services produced.
B) Average price level of goods and services.
C) International value of the dollar.
D) Growth rate of the population.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One World View article is titled "Global Depression." The countries that experienced the Depression
A) Experienced GDP growth but at a rate below the long-term trend.
B) Experienced higher employment levels than previously recorded.
C) Suffered substantial losses of output and employment.
D) Experienced high unemployment but an increase in output.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume you have $2,000 in a savings account at the beginning of the year and the price level is equal to 100.If the price level is equal to 120 at the end of the year,the real value of your savings is closest to
A) $1,667.
B) $1,880.
C) $2,120.
D) $2,400.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about business cycles in the United States?
A) They are remarkably similar in length but vary greatly in intensity.
B) They vary greatly in length,frequency,and intensity.
C) They are similar in frequency and intensity but not in length.
D) They are similar in length,frequency,and intensity.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is generally considered a desirable outcome of government intervention?
A) More jobs.
B) A higher price level.
C) Higher unemployment rates.
D) Greater deficits.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The unique situation in which the behavior of buyers and sellers is compatible is referred to as
A) Full-employment GDP.
B) Macro equilibrium.
C) Micro equilibrium.
D) Labor market balance.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keynesian levers include
A) Deregulation.
B) Fiscal policy.
C) Monetary policy.
D) Aggregate supply.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The laissez faire view of government involvement in the economy is most consistent with the
A) Classical theory.
B) Keynesian theory.
C) Monetary theory.
D) Supply-side theory.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following caused a recession in the years immediately following World War II?
A) A surge in investment spending.
B) Pent-up demand for consumer goods.
C) Cutbacks in defense production.
D) Technological advances.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
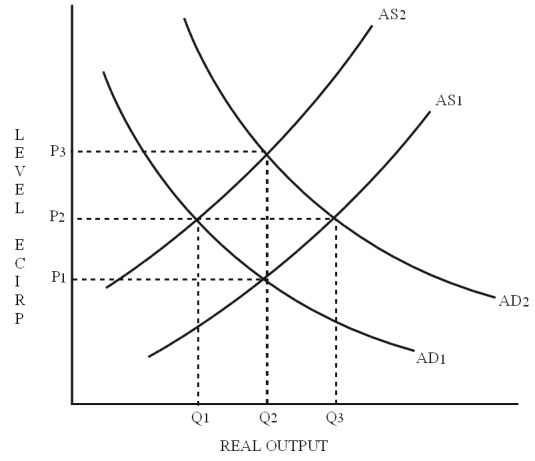 In Figure 8.5,if equilibrium real output is Q1 and full-employment real output is Q2,an appropriate monetarist policy lever would be to increase
In Figure 8.5,if equilibrium real output is Q1 and full-employment real output is Q2,an appropriate monetarist policy lever would be to increase
A) AD by decreasing income taxes.
B) AS by increasing the money supply.
C) AD by reducing interest rates.
D) AD by reducing government regulations.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
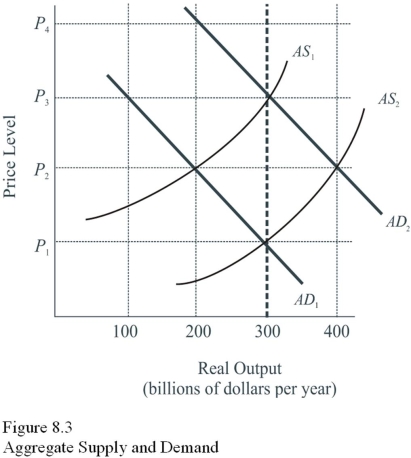 Given AD1 and AS1 in Figure 8.3,the classical approach to achieving full employment at an output of $300 billion would be to
Given AD1 and AS1 in Figure 8.3,the classical approach to achieving full employment at an output of $300 billion would be to
A) Increase taxes and increase government spending to shift AD1 to AD2.
B) Increase the growth of the money supply to shift AD1 to AD2.
C) Do nothing and wait for "natural" market forces to achieve full employment.
D) Use all available supply-side options.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ceteris paribus,if average prices in the U.S.economy fall,then the
A) Real balances effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
B) Foreign trade effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
C) Interest rate effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S.output demanded.
D) Cost effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S.output demandeD.As the price level falls,interest rates fall,so spending on interest-sensitive items such as cars and plasma TVs increases.Even with a constant quantity of nominal money,interest rates fall because a decrease in the price level causes an increase in the supply of real money in a lending institution.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The government can "prime the pump" by doing all of the following except
A) Buying more output.
B) Employing more people.
C) Making more money available.
D) Raising taxes.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 138
Related Exams