A) C2H4
B) C4H8
C) C4H6
D) C4H10
E) C4H2
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The systematic name for the compound represented below is 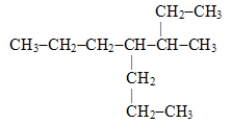
A) 4,5-diethylheptane
B) 3-propyl-4-ethylhexane
C) 3-ethyl-4-propylhexane
D) 3-methyl-4-propylheptane
E) 2-ethyl-4-propylhexane
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the one chiral molecule.
A) CH2Cl2
B) CHFClBr
C) CH3F
D) CHFCl2
E) CH4
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alkenes have the general formula
A) CnH2n-4
B) CnH2n-2
C) CnH2n
D) CnH2n+2
E) CnH2n+4
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which option represents 1,6-hexanediamine?
A) HNCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2NH
B) H2NCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2
C) H2NC(NH2) CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
D) HNC(NH) CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
E) H3N+CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2NH3+
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is the systematic name for the compound represented below? 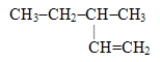
A) 2-ethylbutane
B) 3-methylpentene
C) 3-methyl-1-pentene
D) 3-methyl-1-hexene
E) 2-methylhexane
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxidation of the 2-propanol will produce a/an
A) aldehyde.
B) amine.
C) alkene.
D) ketone.
E) carboxylic acid.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Name the following compound: 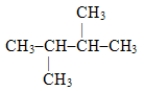
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Name the following compound: 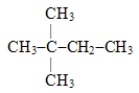
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Which of the following compounds are isomers of each other? I.pentane II.2-methylbutane III.2,3-dimethylbutane IV.2,2-dimethylpropane V.1-hexene
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The reaction of hydrogen chloride gas with propene will yield 1-chloropropane as the main product.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Esters are synthesized from two classes of organic compounds.Those two types of compounds are
A) acids and bases.
B) amines and alcohols.
C) alcohols and acids.
D) amines and alkenes.
E) alkenes and bases.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction of ethylene and water yields
A) an aldehyde.
B) an ester.
C) an alcohol.
D) an ether.
E) an organic acid.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements describes a condensation reaction?
A) addition of H2O to a double bond
B) linking an acid and an alcohol to make an ester and water
C) addition of H2 to an alkene
D) oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde
E) hydrolysis of an ester
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The oxidation product of 1-propanol when using Cr2O72- as the oxidizing agent is acetone.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following functional groups is found in carboxylic acids? 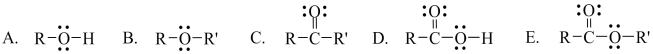
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which option represents dimethyl ether?
A) CH3CH2OH
B) CH3OH
C) CH3COCH3
D) CH3OCH3
E) CH3CH2OCH3
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The formula CH3C CCH3 represents
A) an alkane.
B) a cycloalkane.
C) an alkene.
D) an alkyne.
E) an aromatic compound.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bromination of benzene (C6H6) , an aromatic compound,
A) occurs by substitution rather than addition.
B) occurs by addition rather than substitution.
C) occurs more rapidly than bromination of a nonaromatic compound.
D) results in formation of 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexabromocyclohexane.
E) occurs in the absence of a catalyst.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these reactions leads to a change in the hybridization of one or more carbon atoms?
A) free radical halogenation of an alkane
B) hydrolysis of an ester to yield an acid and an alcohol
C) substitution of an aromatic ring using a halogen
D) oxidation of an alcohol to yield a carboxylic acid
E) neutralization of an amine using a strong mineral acid
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 67
Related Exams