A) a Nash equilibrium
B) a cooperative equilibrium
C) a non-cooperative equilibrium
D) a prisoner's dilemma
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In what way does long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition differ from long-run equilibrium under perfect competition?
A) Firms in perfect competition achieve productive and allocative efficiency while firms in monopolistic competition achieve neither allocative nor productive efficiency.
B) The only difference is that in a monopolistically competitive market there are many brands to choose from while in a perfectly competitive market there is one standard product.
C) Firms in perfect competition achieve productive efficiency while firms in monopolistic competition achieve allocative efficiency.
D) Firms in perfect competition achieve allocative efficiency while firms in monopolistic competition achieve brand efficiency.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market is similar to long-run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market in that in both markets,firms ____________.
A) produce at the minimum point of their average total cost curves
B) produce where price equals marginal cost
C) break even
D) produce where price equals marginal revenue
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run,if the demand curve of a monopolistically competitive firm is tangent to its average total cost curve,then _______.
A) the firm would break even
B) the firm would shut down temporarily
C) the firm would earn enough revenue to cover its variable costs, but not its fixed costs
D) the firm would earn an economic profit
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a dominant strategy?
A) An equilibrium where each firm chooses the best strategy, given the strategies of other firms
B) A strategy chosen by two firms that decide to charge the same price or otherwise not to compete
C) A strategy that is obviously the best for each firm that is a party to a business decision
D) A strategy that is the best for a firm no matter what strategies other firms use
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of a typical firm in a monopolistically competitive industry?
A) Product differentiation allows a successful firm to emerge as a market leader in the industry.
B) All firms have identical cost structures.
C) The more successful firms have an incentive to merge in order to exert greater market power.
D) Each firm acts independently.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Consumers in monopolistically competitive markets face a trade-off between paying prices greater than marginal costs and purchasing products that are more closely suited to their tastes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The study of how people make decisions in situations where attaining their goals depends on their interactions with others is called _______.
A) Nash equilibrium
B) the prisoner's dilemma
C) game theory
D) dominant strategy equilibrium
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 9.5 Table 9.5 shows the demand and cost data facing a monopolistically competitive producer of canvas bags. -Refer to Table 9.5.The firm's profit-maximising or loss-minimising price and quantity are ________.
A) price = $10; quantity = 5
B) price = $12; quantity = 4
C) The firm should shut down temporarily
D) This cannot be determined from the information given.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would not occur as a result of a monopolistically competitive firm suffering a short-run economic loss?
A) The firm could exit the industry in the long run.
B) If the firm does not exit the industry in the long run, its demand curve will shift to the left.
C) If the firm does not exit the industry in the long run, its demand curve will shift to the right.
D) If the firm remains in the industry in the long run, it will break even.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is important in determining the extent of competition in an industry?
A) The minimum level of short-run average total costs of production
B) The minimum efficient scale of production relative to market demand
C) Whether or not the industry product is differentiated or standardised
D) The level of market demand for the industry's product
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolistically competitive firm,marginal revenue _______.
A) equals the price
B) is greater than the price
C) is less than the price
D) and price are unrelated
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9.8 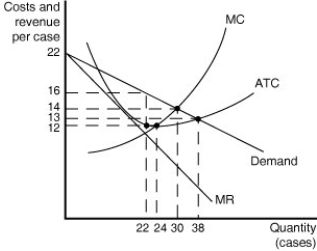 Figure 9.8 shows cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive producer of iced tea.
-Refer to Figure 9.8.The firm's profit-maximising price is ______.
Figure 9.8 shows cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive producer of iced tea.
-Refer to Figure 9.8.The firm's profit-maximising price is ______.
A) $12
B) $13
C) $14
D) $16
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a barrier to entry?
A) An inelastic demand curve
B) Economies of scale
C) Ownership of a key input
D) A patent
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In monopolistic competition,if a firm produces a highly desirable product relative to its competitors,the firm will be able to raise its price without losing any customers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Assume that price exceeds average variable cost over the relevant range of demand.If a monopolistically competitive firm is producing at an output where marginal revenue is $111.11 and marginal cost is $118,then to maximise profits the firm should increase its output.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Nash equilibrium is ______.
A) reached when an oligopoly's market demand and supply intersect
B) reached when each player chooses the best strategy for himself and for the group
C) reached when each player chooses the best strategy for himself, given the other strategies chosen by the other players in the group
D) an equilibrium comprising non-dominant strategies only
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which type of industry is interdependence most common?
A) Monopolistically competitive industries
B) Monopolistic industries
C) Monopolistically competitive and oligopolistic industries
D) Oligopolistic industries
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about monopolistically competitive firms?
A) Unlike perfectly competitive firms, monopolistically competitive firms are able to raise their prices without losing all of their customers.
B) Like perfectly competitive firms, monopolistically competitive firms are not able to raise prices without losing all of their customers because they face competition from firms selling similar products.
C) Like perfectly competitive firms, monopolistically competitive firms maximise their profits by settling price equal to marginal cost.
D) Unlike perfectly competitive firms, monopolistically competitive firms face perfectly inelastic demand curves.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9.4 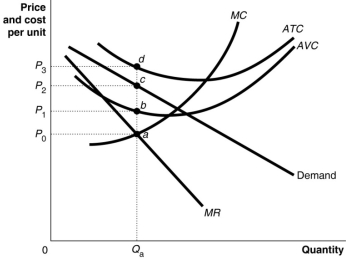 Figure 9.4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
-Refer to Figure 9.4.The area that represents the total variable cost of production is
Figure 9.4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
-Refer to Figure 9.4.The area that represents the total variable cost of production is
A) 0P0aQa
B) 0P1bQa
C) P0abP1
D) P1bdP3
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 350
Related Exams