A) lowering activation energy.
B) adding some energy to the system.
C) increasing activation energy.
D) lowering activation energy and adding some energy to the system.
E) doing all of these.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Answer the questions by matching each word or groups of words with the appropriate definition. a.reactant b.product c.ATP d.activation energy e.reaction f.phosphorylation -the main energy carrier between reaction sites in cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In passive transport,the movement of a small,nonpolar molecule across a cell membrane depends on
A) adequate amounts of ATP.
B) a concentration gradient.
C) adequate ATP and a concentration gradient
D) the proper transport protein.
E) gated channels.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following statements are all true about energy except one.Choose the exception.
A) Energy is captured by heterotrophs.
B) Energy is not recycled.
C) Energy is the ability to do work.
D) Energy has a tendency to disperse.
E) Energy can be transferred from one form to another.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Movement of substances that requires the expenditure of ATP molecules is
A) facilitated diffusion.
B) simple diffusion.
C) active transport.
D) osmosis.
E) bulk flow.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxygen,carbon dioxide,as well as other small molecules,cross the plasma membrane through the process(es) of
A) diffusion.
B) osmosis.
C) endocytosis and exocytosis.
D) active transport.
E) facilitated diffusion.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most toxic?
A) alcohol dehydrogenase
B) ethanol
C) acetaldehyde
D) acetate
E) carbon dioxide
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Passive molecular diffusion occurs when
A) the energy of ATP is added.
B) random collisions between molecules occurs.
C) there are variations in molecular sizes.
D) enzymes catalyze their movement.
E) none of these things occur.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount of turgor that is enough to stop osmosis is called
A) the wilting point.
B) osmotic pressure.
C) hypotonicity.
D) expansion pressure.
E) hypertonicity.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT about energy?
A) Energy is the capacity to do work.
B) It can be created using nuclear reactors.
C) It can be created using a windmill.
D) It can be created using biofuels.
E) All of these are correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is true about guncotton?
A) it is a highly explosive derivative of cholesterol.
B) it is used to make gunpowder.
C) it is less stable than gunpowder
D) it has a higher activation energy for a reaction with oxygen than gunpowder
E) more than one of these is correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Energy
A) cannot be created.
B) cannot be destroyed.
C) cannot be created or destroyed.
D) can be created, but it cannot be destroyed.
E) can be created, and it can be destroyed.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To engulf a bacterium,a white blood cell would use
A) facilitated diffusion
B) osmosis
C) phagocytosis
D) exocytosis
E) sodium-potassium pumps
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Match the following correctly. a.simple diffusion b.exocytosis c.osmosis d.active transport e.phagocytosis -This process explains the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unlike plants,fungi,and bacteria,animal cells cannot resist volume increases in hypotonic environments.This is because unlike those other organisms,animal cells
A) do not have central vacuoles.
B) do not have cell walls.
C) do not have pumps that can actively pump out excess fluid.
D) are smaller than those other cells and thus cannot handle large increases in volume.
E) have relatively more solutes.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate of diffusion across a selectively permeable membrane will be slow when which of the following is (are) true? 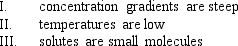
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) I, II, and III
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The second law of thermodynamics implies that
A) energy can be transformed into matter, and because of this, we can get something for nothing.
B) energy can be destroyed during nuclear reactions.
C) if energy is gained by one region of the universe, another place in the universe must also gain energy in order to maintain the balance of nature.
D) energy that is available to do work in the universe is decreasing.
E) energy can be created out of nothing.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The products of a reaction can have less energy than the reactants.
B) The products of a reaction can have more energy than the reactants.
C) Reversible reactions tend to approach equilibrium.
D) Many reactions are reversible.
E) All of these are true.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to survive,heterotrophs must
A) harvest the heat energy that is lost in energy conversions.
B) recycle energy from our metabolic reactions.
C) constantly take in energy rich foods.
D) harvest energy from sunlight.
E) convert low energy molecules into high energy molecules.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tonicity refers to
A) the total concentration of solutes in fluids separated by a selectively permeable membrane.
B) the pressure exerted by the fluids surrounding a cell.
C) the amount of negative versus positive charges of the molecules and ions in a solution.
D) how able a cell is to resist changes in solute concentrations without bursting or shrinking.
E) the ease with which solutes can cross a particular cell membrane.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 107
Related Exams