A) SSB
B) Tus
C) primosome
D) ARS
E) ATS
F) primer
G) transposons
H) nick translation
I) photolyase
J) processive
K) G-loops
L) G-quartets
M) accurate
N) lagging strand synthesis
O) MCM
P) abortive
R) E) and J)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following activities does E.coli DNA polymerase III contain? (I) 5'→3' polymerase (II) 5'→3' exonuclease (III) 3'→5' exonuclease
A) I only
B) I,II
C) II only
D) I,III
E) I,II,III
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Matching Choose the correct answer from the list.Not all the answers will be used. -The process whereby nucleotides are removed from the 5' end of one DNA segment while nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the immediately preceding DNA segment is called ______.
A) SSB
B) Tus
C) primosome
D) ARS
E) ATS
F) primer
G) transposons
H) nick translation
I) photolyase
J) processive
K) G-loops
L) G-quartets
M) accurate
N) lagging strand synthesis
O) MCM
P) abortive
R) G) and L)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Capping is important because
A) it likely protects the telomere ends from becoming shortened.
B) it likely prevents DNA repair mechanisms from initiating at the telomeres.
C) it likely results in increased processivity on the eukaryotic chromosome.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the fidelity of replication is FALSE?
A) Cells maintaining an equal concentration of each dNTP helps maintain fidelity.
B) DNA polymerase catalyzes synthesis in a two-stage reaction,ensuring the proper base is added.
C) Cells viability is removed when DNA point mutations are incorporated.
D) Pol I and Pol III are both involved in increasing fidelity.
E) Specific repair systems repair and maintain DNA.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes the usefulness of primase?
A) It removes RNA bases and replaces them with DNA bases.
B) It seals nicks.
C) It adds an RNA starter sequence which can be elongated.
D) It is only required on the leading strand.
E) It unwinds the DNA.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA ligase can be activated by which of the following? (I) The coupled hydrolysis of NAD+ to (NMN+) + AMP. (II) The coupled hydrolysis of ATP to AMP + PPi. (III) The coupled hydrolysis of GTP to GMP + PPi.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I,II
E) I,III
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A prokaryotic replisome typically contains two molecules of DNA pol III,but only one molecule of DNA pol I.Why?
A) The DNA pol I works on the leading strand,while DNA pol IIIs work on the Okazaki fragments.since there are several of those,it takes more proteins to keep up.
B) DNA pol I has a built-in proofreading exonuclease;DNA pol III does not.The second DNA pol III is needed to follow the first to accomplish the necessary proofreading.
C) The DNA pol IIIs work at one replication fork,while the DNA pol I works at the other.This way they don't meet exactly at the other side of the chromosome.
D) The DNA pol IIIs do most of the work.DNA pol I only has to work on the telomers.
E) DNA pol I replaces the RNA primers with DNA,which really only needs to be done repetitively on one strand,while both strands are worked on by the DNA pol IIIs.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following enzymes catalyze the creation of AP sites for base excision repair?
A) exonuclease
B) endonuclease
C) ligase
D) glycosylase
E) methylase
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Meselson & Stahl had observed the following data in their famous experiment involving a switch from medium containing 15N to 14N.What would they have concluded about the nature of DNA replication? 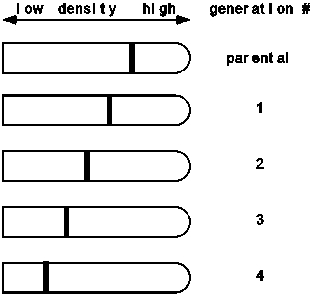
A) They still would have concluded that DNA replication is semiconservative.
B) They would have concluded that DNA replication is conservative.
C) They would have concluded that DNA replication is dispersive/random.
D) None of the above is correct.
E) Cannot be determined with the information given.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about Pol I is FALSE?
A) Experiments demonstrate that Pol I exhibits exonuclease activity.
B) Pol I is not the primary replicase in E.coli.
C) Mutation analysis demonstrates that Pol I functions in DNA repair.
D) Mutation analysis demonstrates the Pol I activity is not essential for cell viability.
E) Experiments have successfully utilized Pol I to radioactively label DNA in lab experiments.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
E.coli leading and lagging strand synthesis takes place at the
A) the Klenow fragment binding site.
B) Pol III & Tus interface.
C) multiprotein replisome.
D) origin recognition complex.
E) telomere.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pol I synthesizes new DNA with very high fidelity,due to its
A) high processivity.
B) 3' 5'exonuclease activity.
C) helicase association with the primase.
D) 5' 3' exonuclease activity.
E) all of the above.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Positive correlations between mutagenesis and carcinogenesis
A) are increased with teleomere capping.
B) are reverted via nick translation.
C) are examined using the Ames test.
D) increase with photoreactivation.
E) None of the above is correct .
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The DNA sequence shown below is copied by the Klenow fragment.Which of the following would most likely result? 5' TGCGTGCACTCGA 3'
A) identical
B) 5' TGCGT 3'
C) 5' TGCAGTGACGCT 3'
D) cannot predict
E) none of the above
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes the Holliday junction?
A) point where DNA base excision repair initiates
B) crossover point involving 4-stranded DNA structure in homologous recombination
C) insertion point of a gene flanked in transposons
D) point where MutS binds to initiate SOS response
E) none of the above
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following diagram to complete the sentences below
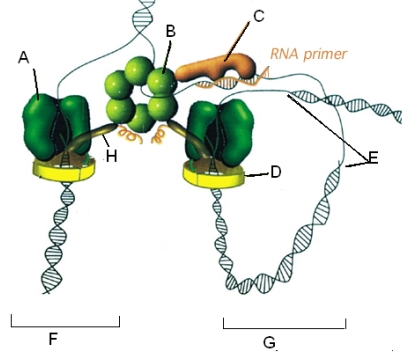 " ______ is the enzyme which catalyzes phosphodiester bond formation on both strands.Processivity of DNA pol is increased when associated with ____.DNA untwisting is accomplished by ______."
" ______ is the enzyme which catalyzes phosphodiester bond formation on both strands.Processivity of DNA pol is increased when associated with ____.DNA untwisting is accomplished by ______."
A) A,C,B
B) A,B,C
C) B,C,A
D) A,D,B
E) A,E,B
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lagging stands are polymerized in the ______ direction,and the DNA fragments are about ______ nucleotides (nt) long in eukaryotic cells.
A) 5' to 3',100-200
B) 5' to 3',1000-2000
C) 3' to 5',100-400
D) 3' to 5',1000-50000
E) none of the above
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Free radical damage to DNA often results in (I) pyrimidine dimers (II) point mutations (III) insertions (IV) base excision
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) I,II.
D) II,III.
E) I,IV.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can be extended by DNA polymerase?
A) a single strand of DNA ending in a nucleotide with a free 3' OH
B) a RNA single strand with a ribonucleotide with a free 3' OH
C) a single strand DNA end in a deoxyribonucleotide with free 5' P
D) a RNA single strand
E) all of the above
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 50
Related Exams