A) I < II < III < IV
B) I < IV < II < III
C) III < II < IV < I
D) II < IV < I < III
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name for the following structure? 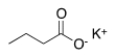
A) Potassium propanoate
B) Butanoic potassium
C) Potassium propanoic
D) Potassium butanoate
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity, putting the most acidic first. 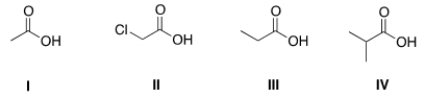
A) IV > III > I > II
B) IV > II > I > III
C) II > I > IV > III
D) II > I > III > IV
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the other product formed in the oxidation of the following terminal alkyne? 
A) HCOOH
B) HCOH
C) CO2
D) CO
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing water solubility, putting the least soluble compound first. 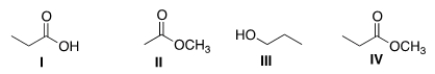
A) I < II < III < IV
B) II < I < III < IV
C) I < III < II < IV
D) IV < II < III < I
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is the C-O single bond of a carboxylic acid shorter than the C-O single bond of an alcohol?
A) The carbon in the alcohol is sp2 hybridized and has a higher percent s-character that lengthens the C-O bond in the alcohol.
B) The carbon in the carboxylic acid is sp3 hybridized and has a lower percent s-character that shortens the C-O bond in the carboxylic acid.
C) The carbon in the carboxylic acid is sp hybridized and has a higher percent s-character that shortens the C-O bond in the carboxylic acid.
D) The carbon in the carboxylic acid is sp2 hybridized and has a higher percent s-character that shortens the C-O bond in the carboxylic acid.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity, putting the least acidic compound first. 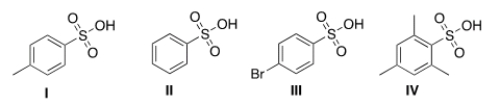
A) III < I < II < IV
B) IV < I < II < III
C) III < II < I < IV
D) II < IV < I < III
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity, putting the least acidic first. 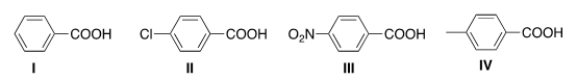
A) I < II < III < IV
B) III < II < I < IV
C) IV < I < II < III
D) I < IV < III < II
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the common name of the following compound? 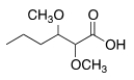
A) ",-Dimethoxyvaleric acid"
B) "2,3-Dimethoxyvaleric acid"
C) "2,3-Dimethoxycaproic acid"
D) ",-Dimethoxycaproic acid"
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What two strong absorptions are characteristic of the IR spectrum of carboxylic acids?
A) A C=O absorption at 1710 cm-1 and a C-H absorption at 3000 cm-1.
B) A C=O absorption at 1710 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3500 cm-1.
C) A C=O absorption at 1600 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3000 cm-1.
D) A C-O absorption at 1500 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3500 cm-1.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As applied to the chemistry of amino acids, what is the definition for the isoelectric point?
A) The pH at which the amino acid exists primarily in its acidic form.
B) The pH at which the amino acid exists primarily in its basic form.
C) The pH at which the amino acid exists as a mixture of isomers.
D) The pH at which the amino acid exists primarily in its neutral form.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following cannot be the starting material for the following reaction? 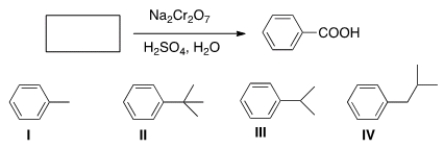
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the common name of the following compound? 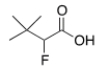
A) ",-Dimethyl--fluorobutyric acid"
B) "-Fluoro-,-dimethylbutyric acid"
C) "-Fluoro-,,-trimethylpropionic acid"
D) "-Fluoro-,,-trimethylbutyric acid"
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following compounds in order of decreasing water solubility, putting the most soluble compound first. 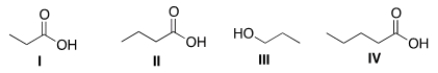
A) I > II > III > IV
B) I > IV > II > III
C) I > II > IV > III
D) IV > III > II > I
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What physical property and reaction type are used by extraction as useful techniques to separate and purify mixtures of compounds?
A) Physical property = solubility differences; reaction type = acid-base reaction.
B) Physical property = boiling point; reaction type = acid-base reaction.
C) Physical property = solubility differences; reaction type = oxidation-reduction.
D) Physical property = density; reaction type = oxidation-reduction.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where do the two noteworthy peaks of carboxylic acids appear in 1HNMR spectra?
A) Between 10 and 12 ppm for the OH proton and 2-2.5 ppm for the protons on the carbon to the carboxy group.
B) Between 6 and 9 ppm for the OH proton and 2-2.5 ppm for the protons on the � carbon to the carboxy group.
C) Between 10 and 12 ppm for the OH proton and 1-1.5 ppm for the protons on the carbon to the carboxy group.
D) Between 6 and 9 ppm for the OH proton and 1-1.5 ppm for the protons on the carbon to the carboxy group.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the correct IUPAC name of the following compound? 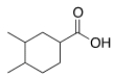
A) 3,4-Dimethylcyclohexanoic acid
B) 3,4-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
C) 4,5-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
D) 1,2-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing acidity, putting the least acidic first. 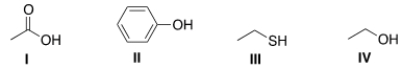
A) I < II < III < IV
B) IV < III < II < I
C) III < IV < II < I
D) IV < II < III < I
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reagents can accomplish the transformation below? ![Which of the following reagents can accomplish the transformation below? A) PCC, CH<sub>2</sub>Cl<sub>2</sub> B) [1] LiAlH<sub>4</sub>, THF; [2] H<sub>2</sub>O C) [1] O<sub>3</sub>; [2] H<sub>2</sub>O D) K<sub>2</sub>Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub>, H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>, H<sub>2</sub>O](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5871/11ea9088_70aa_438d_aec7_6793d282286c_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00.jpg)
A) PCC, CH2Cl2
B) [1] LiAlH4, THF; [2] H2O
C) [1] O3; [2] H2O
D) K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the common name of the following compound? 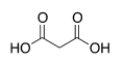
A) Propanedioic acid
B) 1,3-propanedicarboxylic acid
C) Malonic acid
D) Succinic acid
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 44
Related Exams