A) changes an amino acid in the encoded protein
B) has no effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein
C) introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA
D) alters the reading frame of the mRNA
E) prevents introns from being excised
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "universal" genetic code is now known to have exceptions. Evidence for this can be found if which of the following is TRUE?
A) if UGA, usually a stop codon, is found to code for an amino acid such as tryptophan (usually coded for by UGG only) in a different organism
B) if one stop codon, such as UGA, is found to have a different effect on translation than another stop codon, such as UAA
C) if prokaryotic organisms are able to translate a eukaryotic mRNA and produce the same polypeptide
D) if several codons are found to translate to the same amino acid, such as serine
E) if a single mRNA molecule is found to translate to more than one polypeptide when there are two or more AUG sites
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
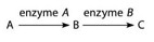 Refer to the metabolic pathway illustrated in the associated figure. If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain mutant for the gene encoding enzyme B would be able to grow on medium supplemented with ________.
Refer to the metabolic pathway illustrated in the associated figure. If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain mutant for the gene encoding enzyme B would be able to grow on medium supplemented with ________.
A) nutrient A only
B) nutrient B only
C) nutrient C only
D) nutrients A and C
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
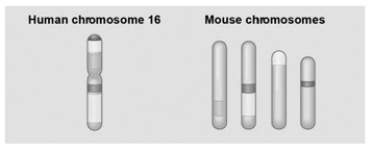 The associated figure shows a diagram of blocks of genes on human chromosome 16 and the locations of blocks of similar genes on four chromosomes of the mouse.
The movement of these blocks suggests that ________.
The associated figure shows a diagram of blocks of genes on human chromosome 16 and the locations of blocks of similar genes on four chromosomes of the mouse.
The movement of these blocks suggests that ________.
A) during evolutionary time, these sequences have separated and have returned to their original positions
B) DNA sequences within these blocks have become increasingly divergent
C) sequences represented have duplicated at least three times
D) chromosomal translocations have moved blocks of sequences to other chromosomes
E) higher mammals have more convergence of gene sequences related in function
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All three domains (Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya) follow the same genetic code. Therefore, which of the following statements would most likely be correct?
A) The genetic code evolved three times.
B) The genetic code evolved before DNA replaced RNA as the unit of genetic information.
C) There were no mutations following the evolution of the genetic code.
D) The genetic code evolved before the different domains diverged.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is TRUE? A codon ________.
A) consists of four nucleotides
B) can code for up to four different amino acids
C) extends from one end of a tRNA molecule
D) is the basic unit of the genetic code
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following nucleotide triplets best represents a codon?
A) a triplet separated spatially from other triplets
B) a triplet in the middle of a ribosomal RNA molecule
C) a triplet at the opposite end of tRNA from the attachment site of the amino acid
D) a triplet in the same reading frame as an upstream AUG
E) a sequence in tRNA at the 3' end
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following contradicts the one-gene, one-enzyme hypothesis?
A) A mutation in a single gene can result in a defective protein.
B) Alkaptonuria results when individuals lack a single enzyme involved in the catalysis of homogentisic acid.
C) Sickle cell anemia results in defective hemoglobin.
D) A single antibody gene can code for different related proteins, depending on the splicing that takes place post-transcriptionally.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most commonly occurring mutation in people with cystic fibrosis is a deletion of a single codon. This results in ________.
A) a base-pair substitution
B) a nucleotide mismatch
C) a frameshift mutation
D) a polypeptide missing an amino acid
E) a nonsense mutation
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Beadle and Tatum discovered that metabolic pathways are studied most effectively using which of the following techniques?
A) using multiple gene mutations resulting in nonfunctional enzymes specific to a metabolic pathway
B) adding intermediates to a metabolic pathway
C) removing all intermediates of a metabolic pathway
D) using single gene mutations resulting in nonfunctional enzymes specific to a metabolic pathway
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which small-scale mutation would be most likely to have a catastrophic effect on the functioning of a protein?
A) a base substitution
B) a base deletion near the start of a gene
C) a base deletion near the end of the coding sequence, but not in the terminator codon
D) deletion of three bases near the start of the coding sequence, but not in the initiator codon
E) a base insertion near the end of the coding sequence, but not in the terminator codon
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
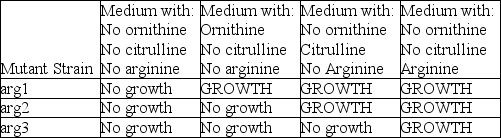
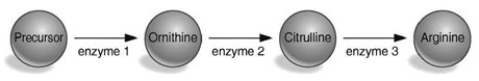 According to the table and the figure associated with this question, which enzyme is defective in the strain with the arg2 mutation?
According to the table and the figure associated with this question, which enzyme is defective in the strain with the arg2 mutation?
A) the enzyme that converts the precursor to ornithine
B) the enzyme that converts ornithine to citrulline
C) the enzyme that converts citrulline to arginine
D) the enzyme that converts the precursor to citrulline
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) refer to this table of codons. 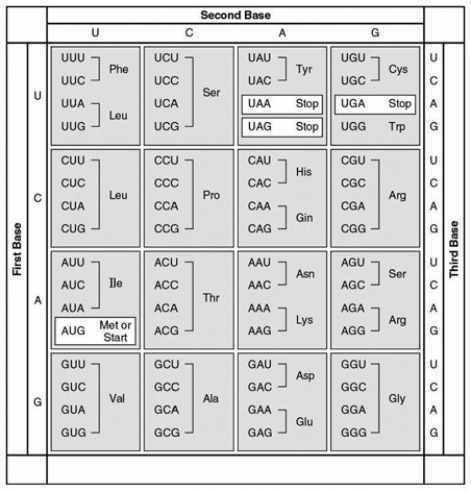 -What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence?
5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
-What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence?
5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
A) met-arg-glu-arg-glu-arg
B) met-glu-arg-arg-glu-leu
C) met-ser-leu-ser-leu-ser
D) met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
E) met-leu-phe-arg-glu-glu
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The statement "DNA → RNA → Proteins" ________.
A) is known as the central dogma
B) depicts the regulation of gene expression
C) is the same in all organisms, as well as viruses and prions
D) describes a series of catalytic reactions
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A frameshift mutation could result from ________.
A) a base insertion only
B) a base deletion only
C) a base substitution only
D) deletion of three consecutive bases
E) either an insertion or a deletion of a base
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following DNA mutations is most likely to damage the protein it specifies?
A) a base-pair deletion
B) an addition of three nucleotides
C) a substitution in the last base of a codon
D) a codon deletion
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
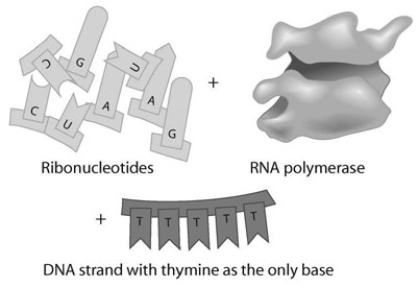 Given the DNA template shown in the associated figure, which of the following bases would you find in a complementary RNA strand and where would they be synthesized?
Given the DNA template shown in the associated figure, which of the following bases would you find in a complementary RNA strand and where would they be synthesized?
A) A-A-A-A-A; nucleus
B) U-U-U-U-U; nucleus
C) A-A-A-A-A; ribosome
D) U-U-U-U-U; ribosome
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From this, one can logically assume which of the following?
A) A gene from an organism can theoretically be expressed by any other organism.
B) All organisms have experienced convergent evolution.
C) DNA was the first genetic material.
D) The same codons in different organisms translate into different amino acids.
E) Different organisms have different types of amino acids.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does it mean when we say the genetic code is redundant?
A) A single codon can specify the addition of more than one amino acid.
B) The genetic code is different for different domains of organisms.
C) The genetic code is universal (the same for all organisms) .
D) More than one codon can specify the addition of the same amino acid.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutations is likely to cause the most dramatic phenotypic change?
A) a duplication of all or most introns
B) a large inversion whose ends are each in the same region between genes
C) a nucleotide substitution in an exon coding for a transmembrane domain
D) a single nucleotide deletion in an exon coding for an active site
E) a frameshift mutation one codon away from the 3' end of the nontemplate strand
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 48
Related Exams