Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Solve the initial-value problem using the method of undetermined coefficients. 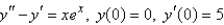
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Solve the differential equation. 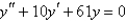
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Solve the differential equation using the method of variation of parameters. 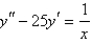
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The solution of the initial-value problem 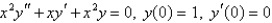 is called a Bessel function of order 0. Solve the initial - value problem to find a power series expansion for the Bessel function.
is called a Bessel function of order 0. Solve the initial - value problem to find a power series expansion for the Bessel function.
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
A spring with a mass of 2 kg has damping constant 14, and a force of 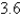 N is required to keep the spring stretched
N is required to keep the spring stretched 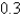 m beyond its natural length. The spring is stretched 1m beyond its natural length and then released with zero velocity. Find the position x(t) of the mass at any time t.
m beyond its natural length. The spring is stretched 1m beyond its natural length and then released with zero velocity. Find the position x(t) of the mass at any time t.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Solve the differential equation. 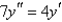
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Solve the differential equation using the method of variation of parameters. 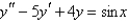
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Solve the initial-value problem. 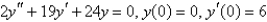
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Solve the initial-value problem. 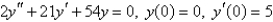
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use power series to solve the differential equation.. 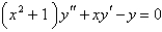
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Solve the differential equation using the method of undetermined coefficients. 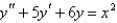
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Solve the differential equation. 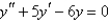
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) None of these
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use power series to solve the differential equation. 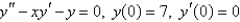
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph the particular solution and several other solutions. 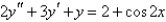
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Solve the initial-value problem. 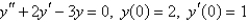
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) None of these
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A spring with a 3-kg mass is held stretched 0.9 m beyond its natural length by a force of 30 N. If the spring begins at its equilibrium position but a push gives it an initial velocity of 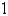 m/s, find the position x(t) of the mass after t seconds.
m/s, find the position x(t) of the mass after t seconds.
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Find a trial solution for the method of undetermined coefficients. Do not determine the coefficients. 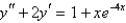
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Solve the differential equation. 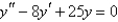
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Solve the initial-value problem. 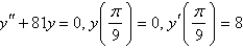
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 63
Related Exams