A) Polar bears can provide more food for humans than seals can.
B) The total biomass of the fish is lower than that of the seals.
C) Seal meat probably contains the highest concentrations of fat-soluble toxins.
D) Seal populations are larger than fish populations.
E) The fish can potentially provide more food for humans than the seal meat can.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the sun were to suddenly stop providing energy to Earth, most ecosystems would vanish. Which of the following ecosystems would likely survive the longest after this hypothetical disaster?
A) tropical rain forest
B) tundra
C) deep-sea hydrothermal vent community
D) grassland
E) desert
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following locations is the largest reservoir for carbon in the carbon cycle?
A) atmosphere
B) sedimentary rocks
C) fossilized plant and animal remains (coal, oil, and natural gas)
D) plant and animal biomass
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Hubbard Brook watershed deforestation experiment yielded all of the following results except:
A) Most minerals were recycled within a forest ecosystem.
B) Calcium levels remained high in the soil of deforested areas.
C) Deforestation increased water runoff.
D) The nitrate concentration in waters draining the deforested area became dangerously high.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. The tundra biome is rapidly changing as a result of global warming. Studying the energy budget of the tundra can help scientists to evaluate the magnitude of these changes. In a randomly selected square meter of tundra, the amount of plant biomass is 200 g. The amount of new plant biomass added in a year is 100 g. In the same square meter, the total biomass added in a year is 15 g. A grasshopper that eats 1 g of plant biomass is able to use 0.15 g of that biomass for growth. The grasshopper cannot assimilate 50% of the plant's biomass. -What is the maximum biomass of grasshoppers that could be supported by this square meter of tundra (i.e., if grasshoppers ate all of the existing vegetation) ?
A) 100 g
B) 50 g
C) 20 g
D) 15 g
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount of chemical energy in a consumer's food that is converted to its own new biomass during a given time period is known as which of the following?
A) biomass
B) standing crop
C) primary production
D) secondary production
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. The tundra biome is rapidly changing as a result of global warming. Studying the energy budget of the tundra can help scientists to evaluate the magnitude of these changes. In a randomly selected square meter of tundra, the amount of plant biomass is 200 g. The amount of new plant biomass added in a year is 100 g. In the same square meter, the total biomass added in a year is 15 g. A grasshopper that eats 1 g of plant biomass is able to use 0.15 g of that biomass for growth. The grasshopper cannot assimilate 50% of the plant's biomass. -What is the production efficiency of the grasshopper?
A) 70%
B) 50%
C) 30%
D) 15%
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The trophic level that ultimately supports all others consists of detritivores.
B) Consumers can exist in an ecosystem without primary producers.
C) Chemoautotrophic prokaryotes near deep-sea vents are primary producers.
D) No losses of energy occur from primary producers in an ecosystem.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of bioremediation?
A) using a bulldozer to reshape the land around an abandoned strip mine to change erosion patterns
B) dredging a river bottom to remove contaminated sediments
C) reconfiguring the channel of a river to increase the flow of water down a river
D) raising chromium-accumulating plants to extract chromium from contaminated soil
E) selectively harvesting younger trees in a forest to leave older trees for woodpecker nesting habitat
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. Starting with the European settlers, humans have introduced earthworms from Europe and Asia into North American forests. These introductions continue through the transport of soil that contains non-native earthworms, such as during construction, and through the release of non-native earthworms used for fishing. The effects of non-native earthworms are especially large in forests that did not have any native earthworms. For example, forests of the Great Lakes region did not previously have earthworms until humans introduced them. When non-native earthworms are introduced, the thick layer of leaf litter disappears quickly, thereby altering biogeochemical cycles. -Which of the following correctly traces a carbon molecule in a Great Lakes forest that is invaded with non-native earthworms?
A) leaf litter → earthworm → soil → trees
B) trees → leaf litter → earthworm → atmosphere
C) bird → earthworm → soil → trees
D) earthworm → fungi → leaf litter → trees
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is primarily responsible for limiting the number of trophic levels in most ecosystems?
A) Many primary and higher-order consumers are opportunistic feeders.
B) Decomposers compete with higher-order consumers for nutrients and energy.
C) Nutrient cycles involve both abiotic and biotic components of ecosystems.
D) Nutrient cycling rates tend to be limited by decomposition.
E) Energy transfer between trophic levels is almost always less than 20% efficient.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of detritivores?
A) They synthesize organic molecules that are used by primary producers.
B) They convert organic materials from all trophic levels to inorganic compounds usable by primary producers.
C) They secrete enzymes that convert the organic molecules of detritus into CO₂ and H₂O.
D) Some species are autotrophic, whereas others are heterotrophic.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has the greatest effect on the rate of chemical cycling in an ecosystem?
A) the rate of decomposition in the ecosystem
B) the production efficiency of the ecosystem's consumers
C) the trophic efficiency of the ecosystem
D) the location of the nutrient reservoirs in the ecosystem
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following organisms is incorrectly paired with its trophic level?
A) cyanobacterium-primary producer
B) grasshopper-primary consumer
C) zooplankton-primary producer
D) fungus-detritivore
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
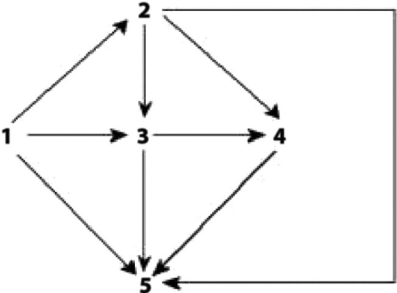 Figure 42.1 Food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem (arrows represent energy flow and numbers represent species)
-Examine the food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem in Figure 42.1. Species C is toxic to predators. Which species is most likely to benefit from being a mimic of C?
Figure 42.1 Food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem (arrows represent energy flow and numbers represent species)
-Examine the food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem in Figure 42.1. Species C is toxic to predators. Which species is most likely to benefit from being a mimic of C?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In ecosystems, why is the term cycling used to describe the transfer of chemical elements, whereas the term flow is used for energy exchange?
A) Chemical elements are repeatedly used, but energy flows through and out of ecosystems.
B) Photosynthesis and feeding relationships result in transforming chemical elements, but not energy.
C) Chemical elements are transferred into ecosystems from other ecosystems, but energy is only transferred within a single ecosystem.
D) In an ecosystem, the total amount of chemical elements does not change, whereas the total amount of energy can change.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
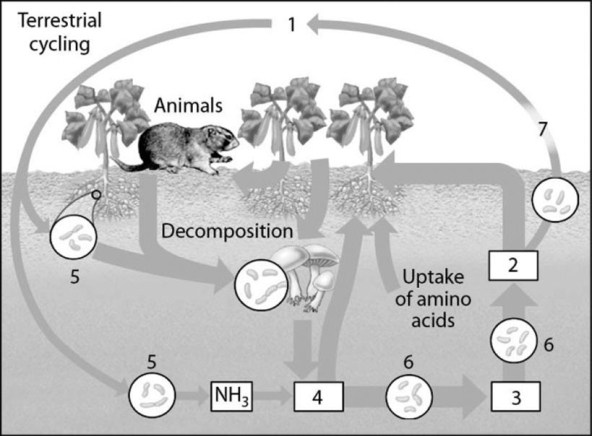 Figure 42.3
-In the diagram of the nitrogen cycle in Figure 42.3, which number represents nitrifying bacteria?
Figure 42.3
-In the diagram of the nitrogen cycle in Figure 42.3, which number represents nitrifying bacteria?
A) 5
B) 6
C) 7
D) 3
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the first step in the restoration of an extremely degraded ecosystem?
A) to restore the physical structure
B) to restore native species that have been extirpated due to disturbance
C) to remove competitive invasive species
D) to identify the limiting factors of the producers
E) to remove toxic pollutants
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To recycle nutrients, an ecosystem must have, at a minimum,
A) producers.
B) producers and decomposers.
C) producers, primary consumers, and decomposers.
D) producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and decomposers.
E) producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, top carnivores, and decomposers.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Approximately how many kilograms of secondary consumer biomass can be supported by a field plot containing 1,000 kg of plant material?
A) 10,000
B) 1,000
C) 100
D) 10
E) 1
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 90
Related Exams