A) tectorial membrane
B) round-window membrane
C) hair cell membrane
D) basilar membrane
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Myasthenia gravis is a form of muscle paralysis in which ________.
A) motor neurons lose their myelination and the ability to rapidly fire action potentials
B) acetylcholine receptors are destroyed by an overactive immune system
C) ATP production becomes uncoupled from mitochondrial electron transport
D) troponin molecules become unable to bind calcium ions
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hair cells in the vertebrate ear are responsible for transducing sound pressure waves. Ion channels in the hair cell membrane open when ________.
A) a chemical ligand binds to the ion channel
B) light is absorbed by a molecule in the membrane
C) the cell membrane reaches a threshold voltage
D) the membrane is distorted mechanically
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The 11 pairs of appendages projecting from the rostral area of star-nosed moles are ________.
A) chemosensory structures
B) tactile structures
C) olfactory structures
D) gustatory structures
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Immediately after putting on a shirt, your skin might feel itchy. However, this perception soon fades due to ________.
A) sensory adaptation
B) accommodation
C) reduced motor unit recruitment
D) reduced receptor amplification
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rods exposed to light will ________.
A) depolarise due to the opening of sodium channels
B) hyperpolarise due to the closing of sodium channels
C) depolarise due to the opening of potassium channels
D) hyperpolarise due to the closing of potassium channels
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct sequence that describes the excitation and contraction of a skeletal muscle fibre? 1) Tropomyosin shifts and unblocks the cross-bridge binding sites. 2) Calcium is released and binds to the troponin complex. 3) Transverse tubules depolarise the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 4) The thin filaments are ratcheted across the thick filaments by the heads of the myosin molecules using energy from ATP. 5) An action potential in a motor neuron causes the axon to release acetylcholine, which depolarises the muscle cell membrane.
A) 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5
B) 2 → 1 → 3 → 5 → 4
C) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1 → 5
D) 5 → 3 → 2 → 1 → 4
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structures would neurobiologists look for if they are interested in determining if an animal can see in colour?
A) opsins
B) electroreceptors
C) pupil
D) lens
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The transduction of sound waves into action potentials occurs
A) in the tectorial membrane as it is stimulated by hair cells.
B) when hair cells are bent against the tectorial membrane, causing them to depolarise and release neurotransmitter that stimulates sensory neurons.
C) as the basilar membrane vibrates at different frequencies in response to the varying volume of sounds.
D) within the middle ear as the vibrations are amplified by the malleus, incus, and stapes.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Statocysts contain cells that are ________.
A) mechanoreceptors used to detect orientation relative to gravity
B) chemoreceptors used in selecting migration routes
C) photoreceptors used in setting biological rhythms
D) thermoreceptors used in prey detection
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Among these choices, the most energetically efficient locomotion per unit mass is likely ________.
A) running by a 50-gram rodent
B) running by a 40-kilogram ungulate
C) flying by a 100-gram bird
D) swimming by a 100-kilogram tuna (bony fish)
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conversion of a stimulus into an action potential by a receptor cell is called ________.
A) integration
B) transmission
C) transduction
D) amplification
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hydrostatic skeleton of the earthworm allows it to move around in its environment by ________.
A) walking on its limbs
B) swimming with its setae
C) using peristaltic contractions of its circular and longitudinal muscles
D) alternating contractions and relaxations of its flagella
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
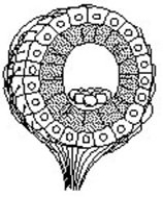 The structure diagrammed in the figure is the ________.
The structure diagrammed in the figure is the ________.
A) neuromast
B) statocyst
C) ommatidium
D) olfactory bulb
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Artificial electrical stimulation of a human's menthol-sensitive neurons would likely produce the sensation of ________.
A) cold temperature
B) hot temperature
C) odour of pepper
D) deep pressure
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dizziness is a perceived sensation that can occur when ________.
A) the hair cells in the cochlea move more than their normal limits
B) moving fluid in the semicircular canals encounters a stationary cupula
C) rods and cones provide information that does not correspond with information received by cochlear hair cells
D) the basilar membrane makes physical contact with the tectorial membrane
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Marine cone snails from the genus Conus are estimated to consist of up to 700 species. These predatory molluscs have devised an efficient venom apparatus that allows them to successfully capture polychaete worms, other molluscs, or in some cases fish as their primary food sources. ) . . conotoxins from Australian species of Conus . . . have the capacity to inhibit specifically the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in higher animals." (B. G. Livett, K. R. Gayler, and Z. Khalil. 2004. Drugs from the sea: Conopeptides as potential therapeutics. Current Medicinal Chemistry 11:1715-23.) -What is the adaptive value of this toxin? I. It would cause muscle spasms in the prey. II. It would result in paralysis of the skeletal muscle of the prey. III. It would stimulate digestive tract smooth muscle to cause nausea and vomiting of the prey.
A) only I
B) only II
C) only III
D) only I and II
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A given photon of light may trigger an action potential with thousands of times more energy because the signal strength is amplified by ________.
A) the receptor
B) ion channels
C) a signal transduction pathway
D) triggering several receptors at once
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The venom of cobras contains a mixture of substances that have a variety of physiological effects. One substance in the venom works by preventing acetylcholine from binding to muscle receptors. How does the venom affect the prey of the cobra?
A) Action potentials would be continuously generated, causing convulsive muscle contractions.
B) Muscle contractions would be prevented, causing paralysis.
C) Muscle contractions could still occur, but relaxation of the muscle would be impaired.
D) Action potentials would be continuously generated, causing convulsive muscle contractions; muscle contractions would then be prevented, causing paralysis.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of receptor would you expect to be most abundant in the antennae of a moth?
A) thermoreceptors
B) mechanoreceptors
C) chemoreceptors
D) electroreceptors
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 67
Related Exams