A) 5′-UTR I1 I2 I3 UTR-3′
B) 5′-E1 E2 E3 E4-3′
C) 5′-UTR E1 E2 E3 E4 UTR-3′
D) 5′-E1 I1 E2 I2 E3 I3 E4-3′
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
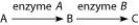 The figure shows a simple metabolic pathway.
-If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain that is mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme A would be able to grow on medium supplemented with which of the following nutrient(s) ?
The figure shows a simple metabolic pathway.
-If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain that is mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme A would be able to grow on medium supplemented with which of the following nutrient(s) ?
A) nutrient A only
B) either nutrient B or C
C) nutrient C only
D) nutrients A and C
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which component is not directly involved in translation?
A) GTP
B) DNA
C) tRNA
D) ribosomes
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules are required for the process of translation?
A) mRNA, tRNA, DNA, and rRNA
B) mRNA, DNA, and rRNA
C) mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
D) mRNA, tRNA, and DNA
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes occurs in eukaryotic gene expression?
A) mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are translated.
B) RNA polymerase binds to the terminator sequence.
C) A cap is added to the 5′ end of the mRNA.
D) RNA polymerase requires tRNA to elongate the molecule.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following DNA mutations is most likely to damage the protein it specifies?
A) a base-pair deletion
B) an addition of three nucleotides
C) a substitution in the last base of a codon
D) a codon deletion
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the release factor during translation in eukaryotes?
A) It binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of a tRNA.
B) It releases the amino acid from its tRNA to allow the amino acid to form a peptide bond.
C) It supplies a source of energy for termination of translation.
D) It releases the ribosome from the ER to allow polypeptides into the cytosol.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutations would be most likely to have a harmful effect on an organism?
A) a deletion of three nucleotides near the middle of a gene
B) a single nucleotide deletion in the middle of an intron
C) a single nucleotide deletion near the end of the coding sequence
D) a single nucleotide insertion downstream of, and close to, the start of the coding sequence
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A part of an mRNA molecule with the following sequence is being read by a ribosome: 5′-CCG-ACG-3′ (mRNA) . The following charged transfer RNA molecules (with their anticodons shown in the 3′ to 5′ direction) are available. Two of them can correctly match the mRNA so that a dipeptide can form. - Which of the following dipeptides will form from this mRNA?
A) cysteine-alanine
B) proline-threonine
C) glycine-cysteine
D) alanine-alanine
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the structural organisation of many eukaryotic genes, individual exons may be related to which of the following?
A) the sequence of the intron that immediately precedes each exon
B) the number of polypeptides making up the functional protein
C) the various domains of the polypeptide product
D) the number of start sites for transcription
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the effect a nonsense mutation would have on a gene?
A) It changes an amino acid in the encoded protein.
B) It has no effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein.
C) It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA.
D) It alters the reading frame of the mRNA.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
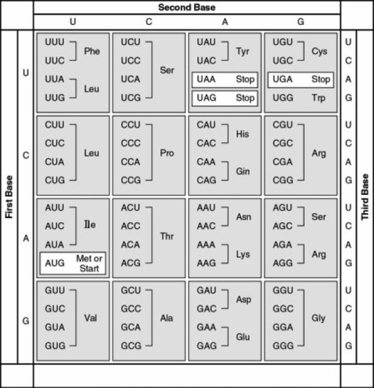 - Which of the following sequences of nucleotides are possible in the template strand of DNA that would code for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Leu-Ile-Val?
- Which of the following sequences of nucleotides are possible in the template strand of DNA that would code for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Leu-Ile-Val?
A) 5′-TTG-CTA-CAG-TAG-3′
B) 5′-AUG-CTG-CAG-TAT-3′
C) 3′-AAA-AAT-ATA-ACA-5′
D) 3′-AAA-GAA-TAA-CAA-5′
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements supports the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis?
A) A mutation in a single gene can result in a defective protein.
B) Alkaptonuria results when individuals lack multiple enzymes involved in the catalysis of homogentisic acid.
C) Sickle-cell anaemia results in normal haemoglobin.
D) Multiple antibody genes can code for different related proteins, depending on the splicing that takes place post-transcriptionally.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes occurs during transcription?
A) DNA is replicated
B) RNA is synthesised
C) proteins are synthesised
D) mRNA attaches to ribosomes
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following structures, if missing, would usually prevent translation from starting?
A) exon
B) 5′ cap
C) AUG codon
D) poly-A tail
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the primary transcript in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell compare to the functional mRNA?
A) the primary transcript is the same size as the mRNA
B) the primary transcript is larger than the mRNA
C) the primary transcript is smaller than the mRNA
D) both the primary transcript and mRNA contain introns
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Codons are three-base sequences in mRNA that specify the addition of a single amino acid to the growing protein chain during translation. How do eukaryotic codons and prokaryotic codons compare?
A) Prokaryotic codons usually contain different bases than those of eukaryotes.
B) Prokaryotic codons usually specify different amino acids than those of eukaryotes.
C) The translation of codons is mediated by tRNAs in eukaryotes, but translation requires no intermediate molecules such as tRNAs in prokaryotes.
D) Codons are a nearly universal language among all organisms.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 - Refer to the figure. Which of the triplets below is a possible anticodon for a tRNA that transports proline to a ribosome?
- Refer to the figure. Which of the triplets below is a possible anticodon for a tRNA that transports proline to a ribosome?
A) 3′-UUC-5′
B) 3′-CCG-5′
C) 3′-GGC-5′
D) 3′-CCC-5′
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of mutation, resulting in an error in the mRNA just after the AUG start of translation, is likely to have the most serious effect on the polypeptide product?
A) a deletion of a codon
B) a deletion of two nucleotides
C) a substitution of the third nucleotide in an ACC codon
D) a substitution of the first nucleotide of a GGG codon
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
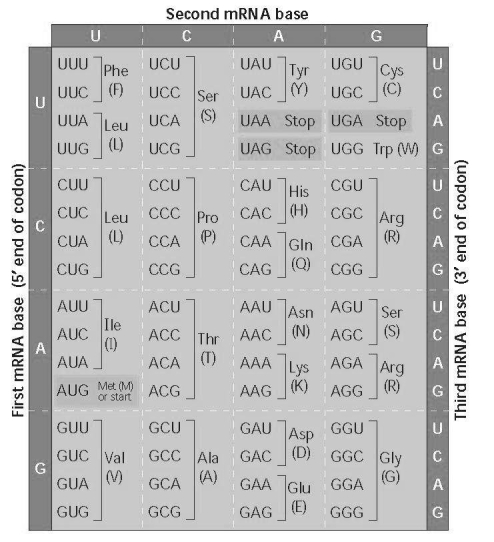 Use the figure to identify a 5′ → 3′ sequence of nucleotides in the DNA template strand for an mRNA coding for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Pro-Lys.
Use the figure to identify a 5′ → 3′ sequence of nucleotides in the DNA template strand for an mRNA coding for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Pro-Lys.
A) 5-UUUCCCAAA-3
B) 5-GAACCCCTT-3
C) 5-CTTCGGGAA-3
D) 5-AAACCCUUU-3
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 67
Related Exams