A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the functional groups is not reactive but serves as a recognisable tag on the DNA molecule and alter the expression of genes in the cells?
A) amino
B) methyl
C) carboxyl
D) hydroxyl
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The kind and number of bonds an atom can form depends on ________.
A) its atomic number
B) its electron configuration
C) its atomic mass
D) the number of particles in its nucleus
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A.
B. 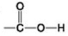 C.
D.
- Which functional group shown can pick up protons and raise the pH of the surrounding solution?
C.
D.
- Which functional group shown can pick up protons and raise the pH of the surrounding solution?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the pairs of molecular structures shown depict enantiomers (enantiomeric forms) of the same molecule?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A.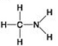 B.
B.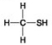 C.
C.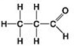 D.
D.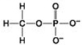 -Which molecule can be a result of mercaptoethanol reduction of a disulphide bridge?
-Which molecule can be a result of mercaptoethanol reduction of a disulphide bridge?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Research indicates that ibuprofen, a drug used to relieve inflammation and pain, is a mixture of two enantiomers; that is, molecules that ________.
A) have identical chemical formulas but differ in the branching of their carbon skeletons
B) are mirror images of each other
C) differ in the location of their double bonds
D) differ in the arrangement of atoms around their double bonds
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules is polar? C3H7OH C2H5COOH
A) C3H7OH and C2H5COOH are both polar molecules.
B) Neither C2H5COOH or C3H7OH is polar.
C) C2H5COOH is polar, but C3H7OH is not polar.
D) C2H5COOH is not polar, but C3H7OH is polar.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A.
B.  C.
D.
- Which of the functional groups shown helps stabilise proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between protein molecules?
C.
D.
- Which of the functional groups shown helps stabilise proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between protein molecules?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids?
A) carbonyl and amino groups
B) carboxyl and amino groups
C) amino and sulfhydryl groups
D) hydroxyl and carboxyl groups
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which action could produce a carbonyl group?
A) the replacement of the -OH of a carboxyl group with hydrogen
B) the addition of a thiol to a hydroxyl
C) the addition of a hydroxyl to a phosphate
D) the replacement of the nitrogen of an amine with oxygen
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some carbon skeletons have different numbers and locations of double bonds to ________.
A) add molecular complexity and diversity that characterise living matter
B) be more flexible that makes the molecule stronger
C) stay in its liquid state
D) increase its solubility in water
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A.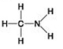 B.
B.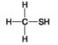 C.
C.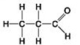 D.
D.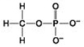 -Which molecules shown contain a carbonyl group?
-Which molecules shown contain a carbonyl group?
A) A and B
B) B and C
C) B, C and D
D) C and D
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with other atoms?
A) ionic
B) hydrogen
C) covalent
D) ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules is a part of ATP?
A) adenosine
B) cytosine
C) guanine
D) uracil
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Amino acids are acids because they always possess ________ as the functional group.
A) amino
B) carbonyl
C) carboxyl
D) phosphate
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the term that correctly describes the relationship between these two sugar molecules: 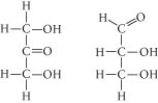
A) structural isomers
B) cis-trans isomers
C) enantiomers
D) isotopes
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The experimental approach taken in current biological investigations presumes that ________.
A) simple organic compounds can be synthesised in the laboratory from inorganic precursors, but complex organic compounds like carbohydrates and proteins can be synthesised only by living organisms
B) a life force ultimately controls the activities of living organisms, and this life force cannot be studied by physical or chemical methods
C) living organisms are composed of the same elements present in nonliving things, plus a few special trace elements found only in living organisms or their products
D) living organisms can be understood in terms of the same physical and chemical laws that can be used to explain all natural phenomena
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What determines whether a carbon atom's covalent bonds to other atoms are in a tetrahedral configuration or a planar configuration?
A) the presence or absence of bonds with oxygen atoms
B) the presence or absence of double bonds between the carbon atom and other atoms
C) the polarity of the covalent bonds between carbon and other atoms
D) the solvent in which the organic molecule is dissolved
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which chemical group is most likely to be responsible for an organic molecule behaving as a base?
A) hydroxyl
B) carbonyl
C) amino
D) phosphate
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 58
Related Exams