A) expansionary fiscal policy.
B) contractionary fiscal policy.
C) expansionary monetary policy.
D) contractionary monetary policy.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the main difficulties with implementing fiscal policy is:
A) the time lag between the time the policy is chosen and the time it gets enacted.
B) deciding on a policy without all the relevant information.
C) the danger in overshooting or undershooting the goal of full employment.
D) All of these are true.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Discretionary fiscal policy is:
A) fiscal policy that the government actively chooses to adopt.
B) taxes and government spending that affect fiscal policy without specific action from policymakers.
C) fiscal policy that the government enacts only for a short period of time.
D) taxes and government spending that the government actively votes against adoption.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
We use the term expansionary fiscal policy when the overall effect of decisions about taxation and spending is to:
A) increase aggregate demand.
B) decrease aggregate demand.
C) increase aggregate supply.
D) decrease aggregate supply.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a recession, government deficits can grow because:
A) government spending often increases as part of an expansionary fiscal policy.
B) income tax revenues tend to decrease because people are earning less.
C) sales tax revenues tend to decrease because people are spending less.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a severe recession, the government decides to lower its tax rates to give consumers relief, and allow them to pay less in taxes. This is an example of:
A) discretionary fiscal policy.
B) an automatic stabilizer.
C) contractionary fiscal policy.
D) expansionary fiscal policy.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The stimulus strategy behind tax cuts will only be effective if Ricardian equivalence:
A) holds, and people increase their spending.
B) holds, and people save more.
C) fails to hold, and people increase their spending.
D) fails to hold, and people save more.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an economy is in an economic boom, discretionary fiscal policy would call for _____________, and the automatic stabilizers would _____________.
A) lowering tax rates; lower tax revenues
B) lowering tax revenues; lower tax rates
C) increasing tax rates; increase tax revenues
D) increasing tax rates; lower tax revenues
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the government enacts fiscal policy, it:
A) may not always be able to improve matters.
B) might make things worse.
C) can bring the economy to its long-run equilibrium more quickly than it can correct itself.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government were to increase its spending, it would expect:
A) aggregate demand to shift to the right.
B) aggregate demand to shift to the left.
C) aggregate supply to shift to the right.
D) aggregate supply to shift to the left.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economist John Maynard Keynes once said, "In the long run, we are all dead." Keynes was likely:
A) in favor of using fiscal policy.
B) against the use of fiscal policy.
C) in favor of allowing the economy to always correct itself.
D) Economy never achieves its long run equilibrium.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One way fiscal policy affects aggregate demand is:
A) directly through government spending.
B) directly through tariffs.
C) directly through taxation.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a benefit of giving the government freedom to spend more than they receive in taxes and run a deficit?
A) It allows the government to be flexible if something unexpected happens.
B) It can make it more difficult for businesses and consumers to borrow.
C) There is never a good enough reason to allow public debt.
D) The federal government cannot run a deficit.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rising unemployment and decreased business confidence could be signs that the economy is at the start of a(n) :
A) recession.
B) boom.
C) recovery.
D) expansion.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
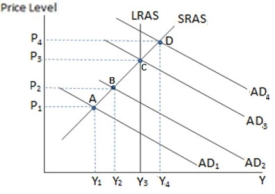 If the economy in the graph shown is currently at point B, and the government enacts contractionary fiscal policy, in the short run the economy will most likely move to point:
If the economy in the graph shown is currently at point B, and the government enacts contractionary fiscal policy, in the short run the economy will most likely move to point:
A) A
B) It is likely to be unaffected and stay at point B
C) C
D) D
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increased government spending on unemployment insurance during a recession is an example of:
A) an automatic stabilizer.
B) discretionary fiscal policy.
C) expansionary fiscal policy.
D) contractionary fiscal policy.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since 1940 the US Government has generally had a budget:
A) surplus.
B) that has been balanced
C) multiplier.
D) deficit.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiscal policy that the government actively chooses to adopt is called:
A) automatic stabilizing policy.
B) discretionary fiscal policy.
C) monetary policy.
D) contractionary policy.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When fiscal policy makers wish to reduce aggregate demand, they could enact:
A) contractionary fiscal policy.
B) expansionary fiscal policy.
C) contractionary monetary policy.
D) expansionary monetary policy.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If interest rates increase, the government debt becomes:
A) more expensive to pay.
B) less expensive to pay.
C) more volatile.
D) less of a burden.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 115
Related Exams